Wouldn’t it be amazing if there’s life on planets other than Earth? We can have our living twins on any other galaxy having a different kind of life than us. What if it’s not just the imagination but a reality?
Scientists have always been busy trying to find life on different planets. Mars is one of the hot areas of research and study. To investigate the possibility of extraterrestrial life, NASA is planning to send a Robotic Rover to Mars in the year 2020. This rover will be equipped with instruments to detect if there are any signs of life on the Red planet.
Instruments
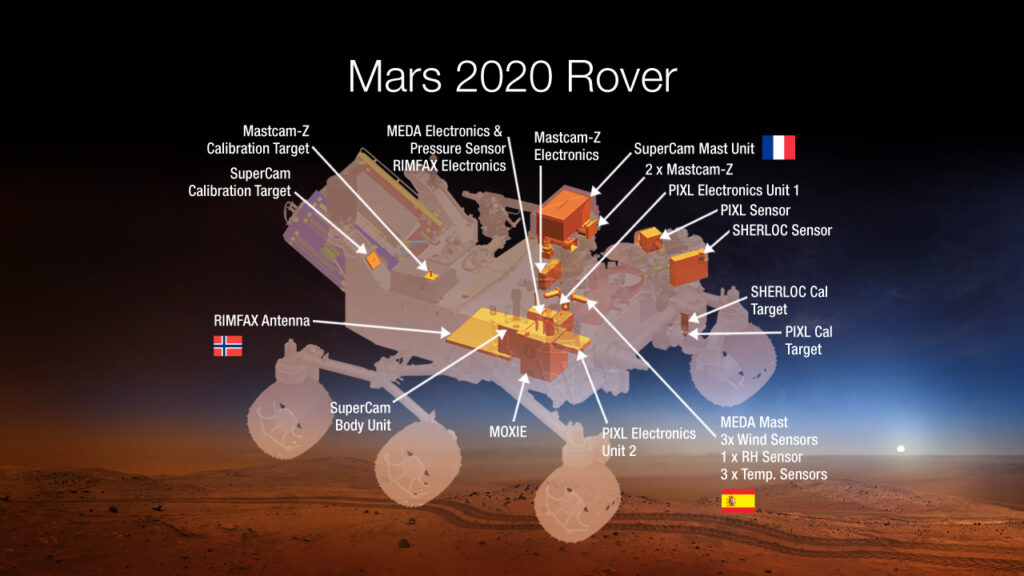
The two main important instruments will be the SHERLOC and Cal target.

• SHERLOC
It will be the big device detecting chemicals which are linked to the existence of life on the Red planet. It is an acronym for Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals (SHERLOC). It consists of a laser, camera, and spectrometer; the chemical analyzer. The components will function to detect the possibility of microscopic life on the planet by substances which are altered by the water. This device is mounted on the 7-foot long robotic arm of the Mars 2020 rover. ARES scientist Marc Fries, the co-investigator of the mission said, “SHERLOC is pretty complicated, and we came up with a list of 11 things that all have to be calibrated on this instrument.”
• Cal target
Cal target is a short term for calibration target. It is another device built on the Mars 2020 rover by Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science (ARES) division at NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC). The main function of the device is to keep an eye on SHERLOC. Being the size of a large mobile phone, Cal target contains 10 target samples of various materials which will be used to check SHERLOC functioning. The basic idea of Cal target according to Trevor Graff, a scientist working for ARES was, “The rover’s scientific instruments go through all sorts of harsh conditions from the time they leave the lab until they arrive on the surface of Mars. SHERLOC needed a way to make sure it still operates as expected once it’s on the surface and throughout the mission.”
The scientists will scan the materials sample on Cal target to detect readings. They will be taught what the readings mean, whether SHERLOC is functioning or not and how to adjust SHERLOC back to its working state if any malfunctioning occurs.
Future Aspects
The Cal device is made multi-functional to serve various purposes instead of just scanning for SHERLOC.
• It has a sample for spacesuit material. Thus, in addition to scanning SHERLOC, it can reveal what strength of fabric can survive in the Planet atmosphere which will, in turn, help to produce spacesuits for astronauts that will protect them in their future visits.
• Another target sample is the actual meteorite ejected from Mars and found on Earth in 1999. It will be used to study the chemical interactions of Martian planet surface and its atmosphere by how the environment alters it over a specific period.
These devices are indeed beneficial and if successful will give a solid explanation of life on the Red planet.

Rida Nayyab is a young activist and a Cricket freak. She is a Student of Bio-Chemistry and striving for a better future. Rida is also a freelance writer, social enthusiast, and love to reading, writing and exploring. She is head of the social media team of Scientia magazine.

