
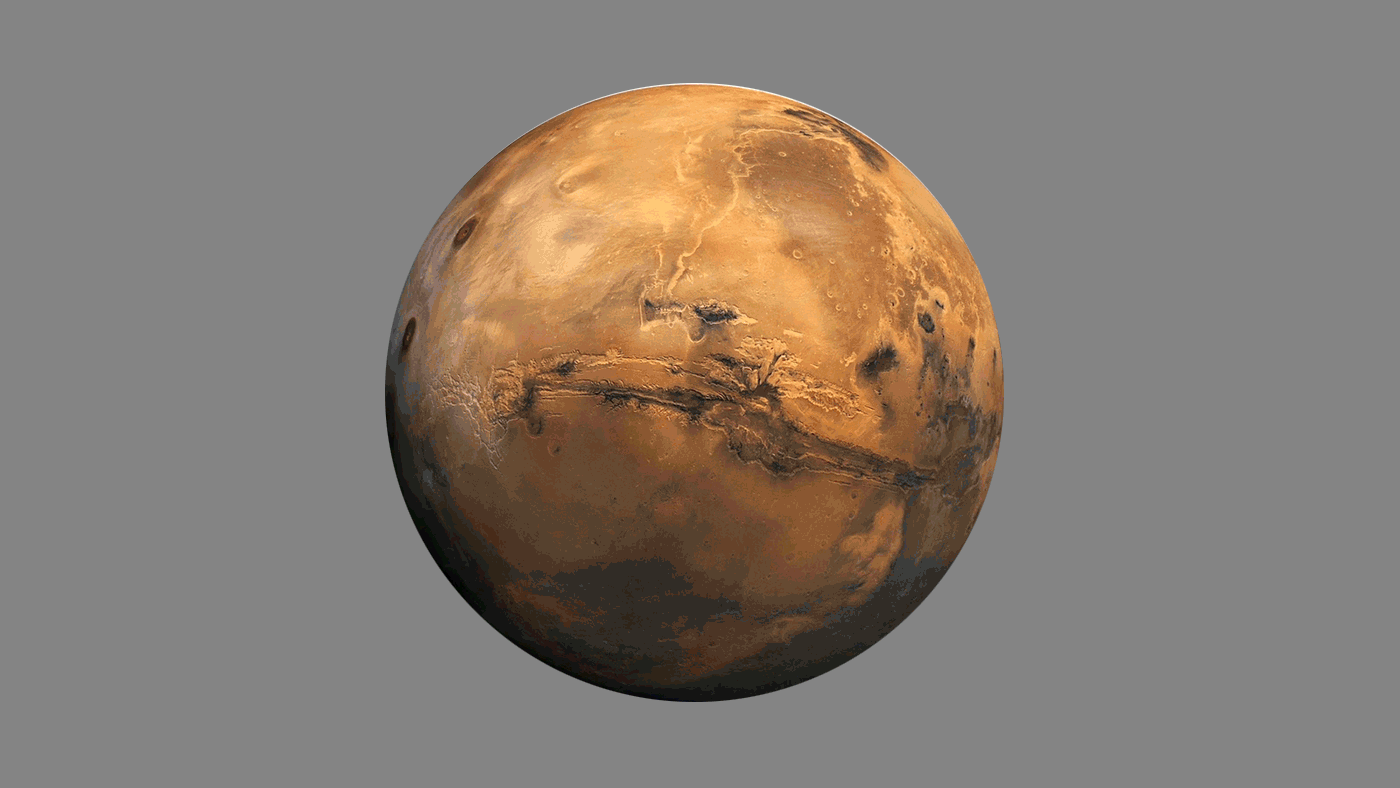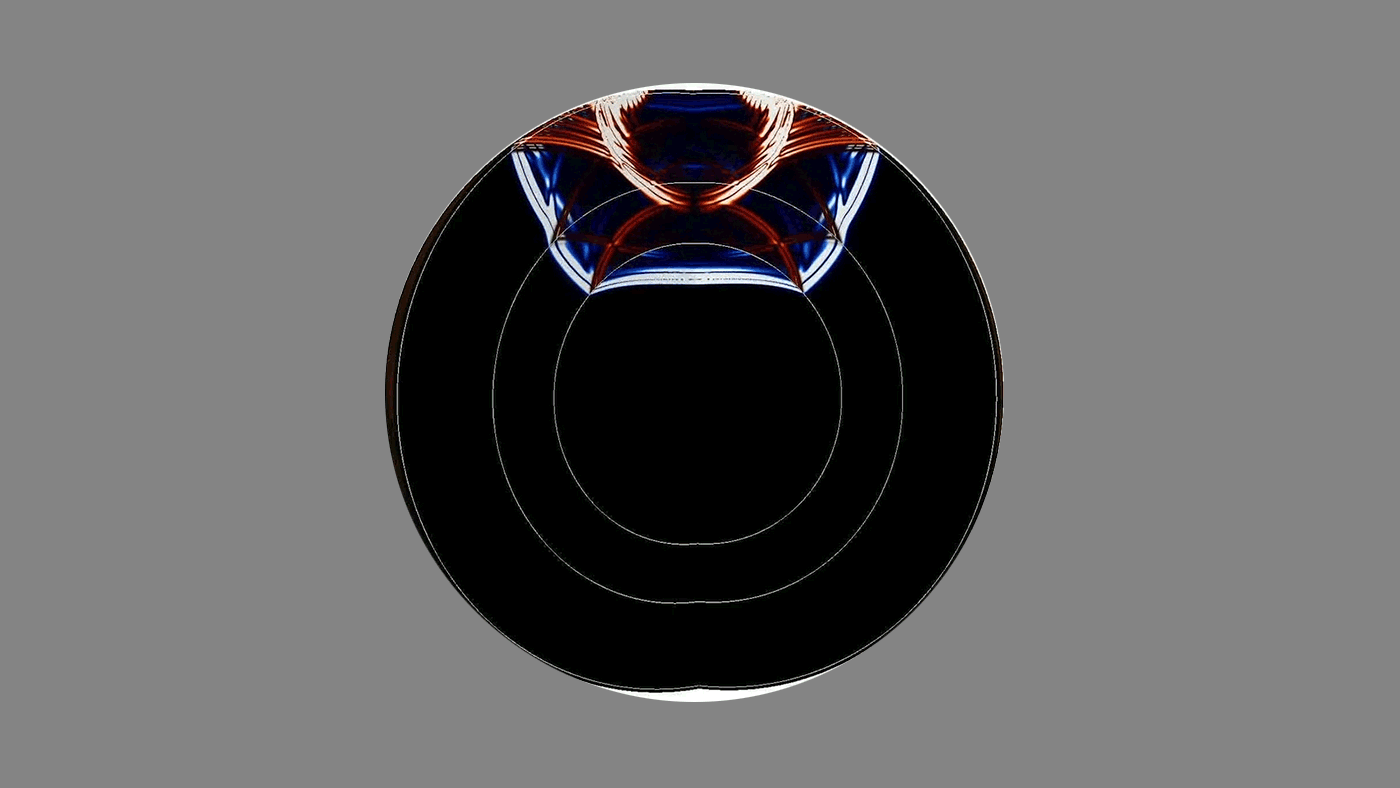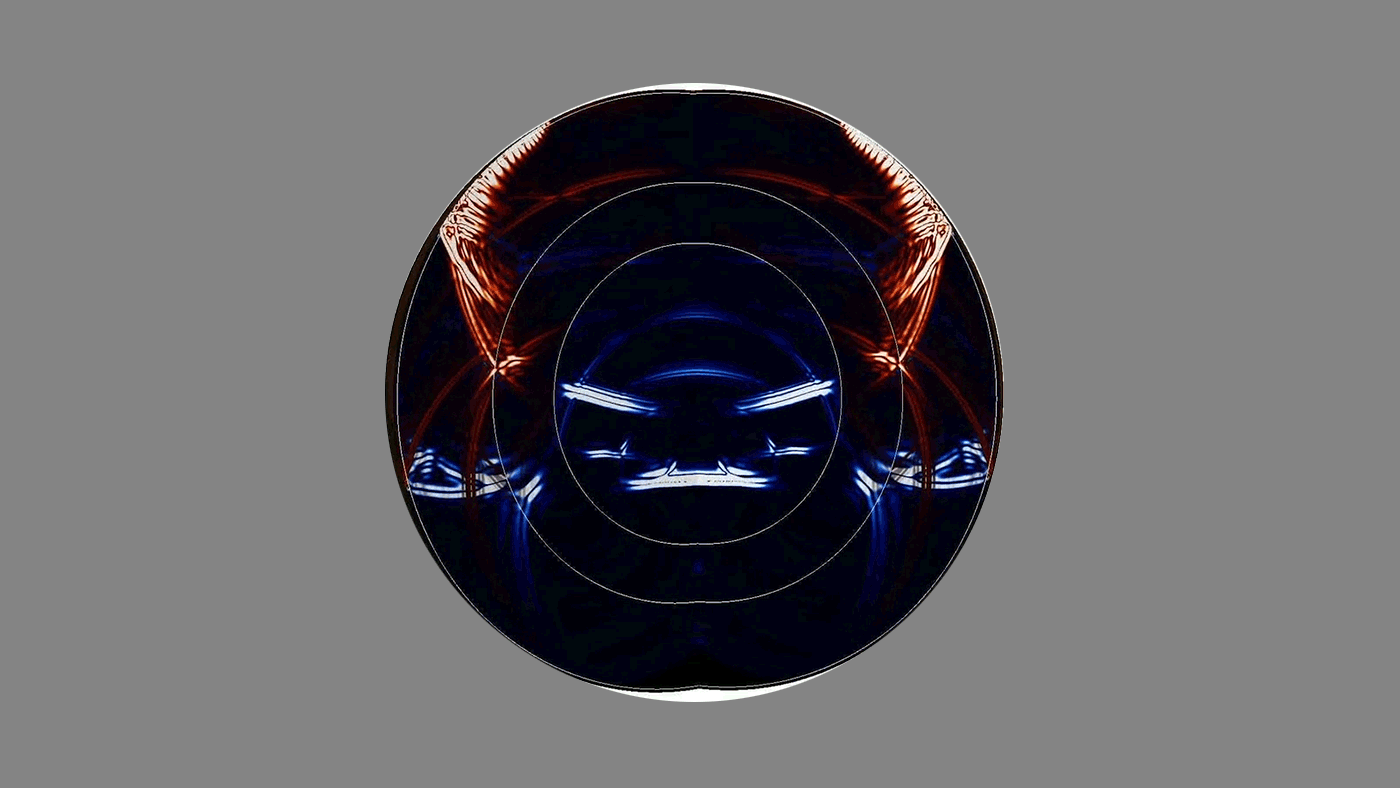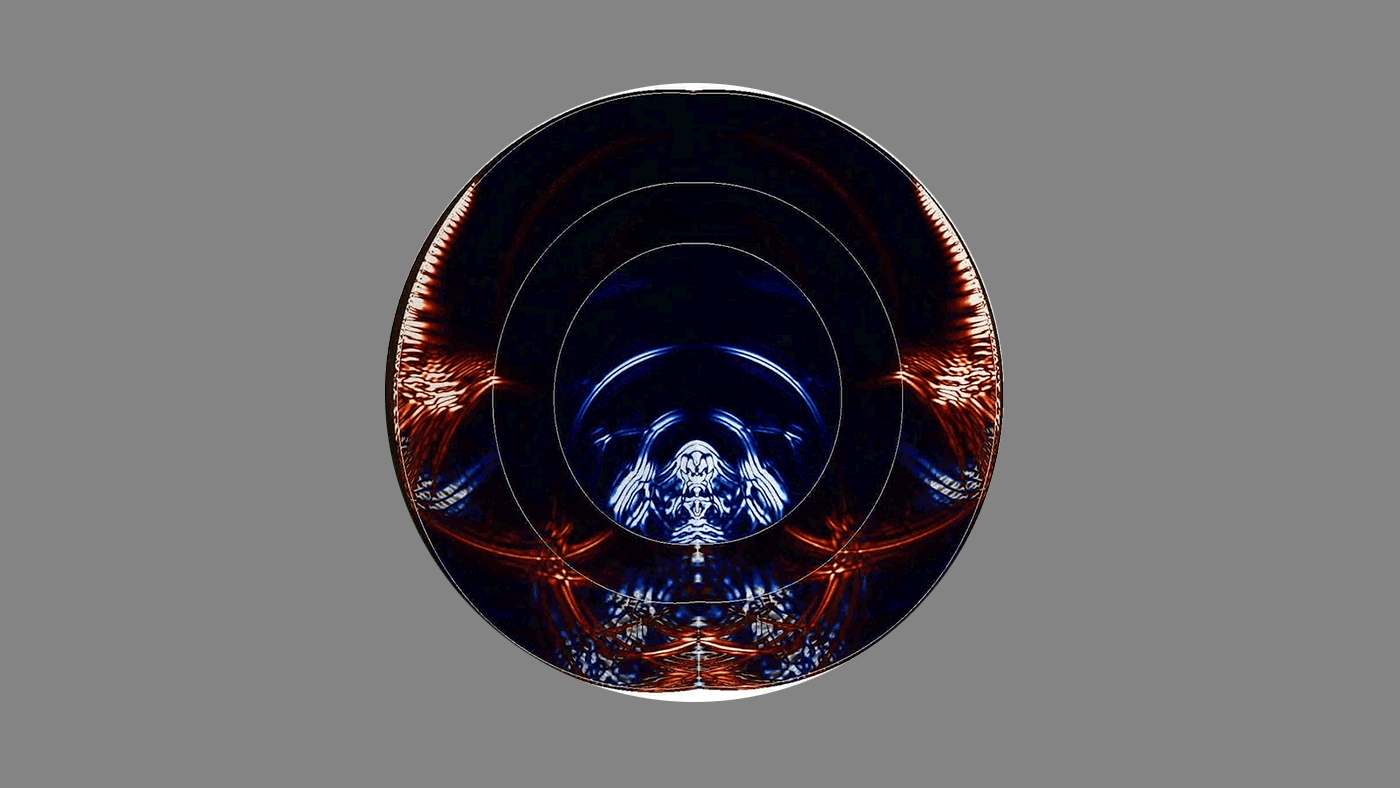
The quest to find life beyond the Earth remains a paramount goal for humanity, with Mars consistently captivating our attention as a prime candidate for exploration. Recently, NASA’s Perseverance rover has made remarkable discoveries that bring us closer to addressing the enduring question: Are we alone in the Universe?
Perseverance has captivated the world’s attention with its latest discovery- a mysterious rock nestled in the dusty Martian surface, named “Cheyava Falls”, which hints at the possibility of past microbial life along with traces of water beneath the crust. This groundbreaking discovery results from the rover’s careful analysis of the rock’s distinctive chemical composition and patterns of traces found, generating excitement among scientists and space enthusiasts.
The Intriguing Discovery of Cheyava Falls
Perseverance came across a particularly intriguing rock, about 1m long and 60cm wide, named “ Cheyava Falls.” Cheyava Falls was found in the mouth of the Jezero crater, which is believed to have been a lake 3.5 billion years ago. According to NASA, “This rock contains fascinating traits that may bear on a question of whether Mars was home to microscopic life in the distant past.”
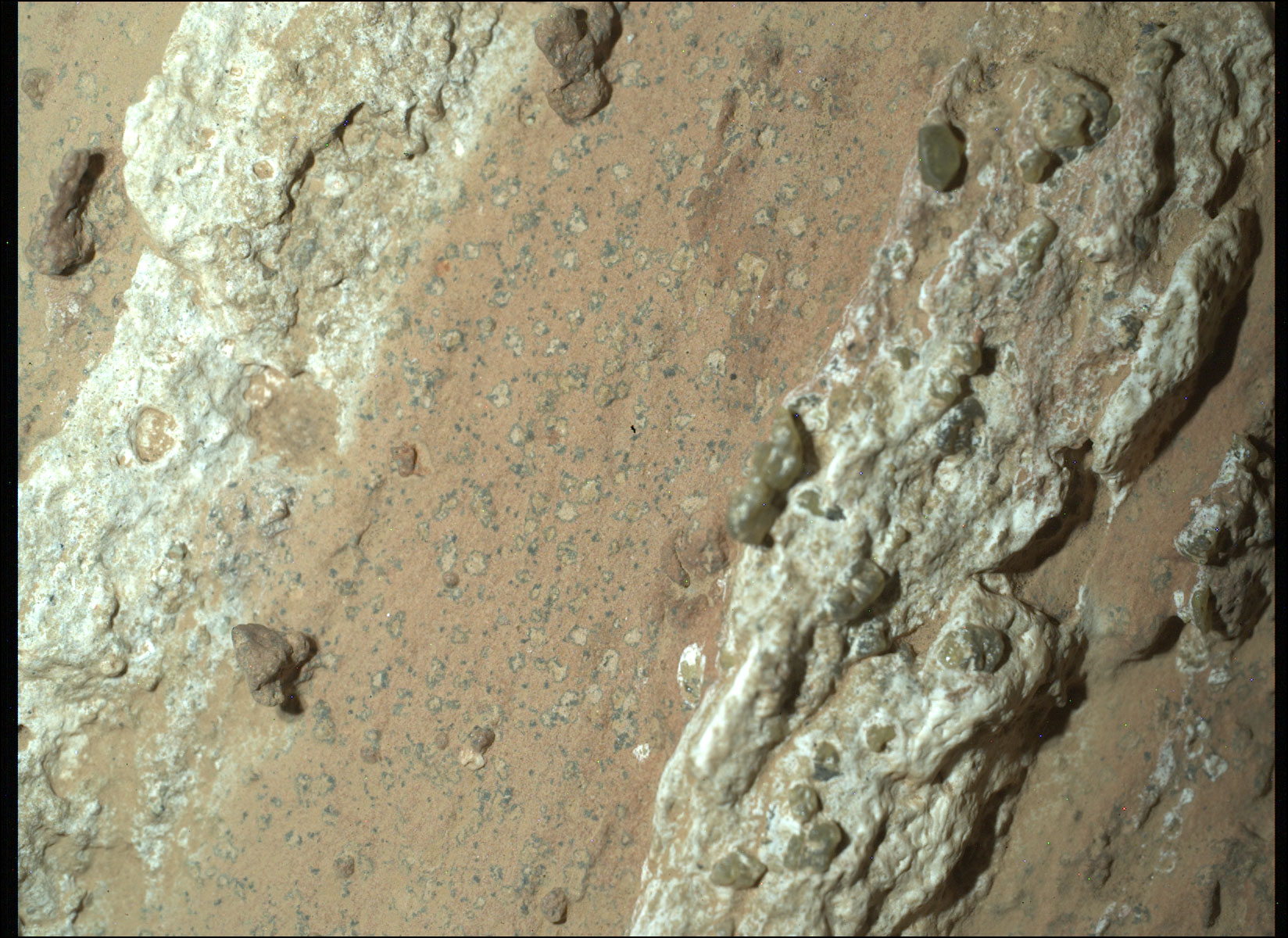

This rock has three distinct features that captivated that attracted scientists. The first is the two long bands of light-colored rock on either side of the above view. The whitish veins of calcium sulfate (Gypsum), running through Cheyava Falls indicate that water once flowed through it.
The second is the detection of organic compounds in the darker reddish band of rock by Perservance’s SHERLOC(Scanning Habitable Environments With Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals) instrument. Organic compounds are those containing carbon, an essential building -block of life as we know it. It is possible that these compounds were the result of some geological process, like if microbes lived in those sediments and later died, when the planet dried up, leaving traces of life activity as evidence.
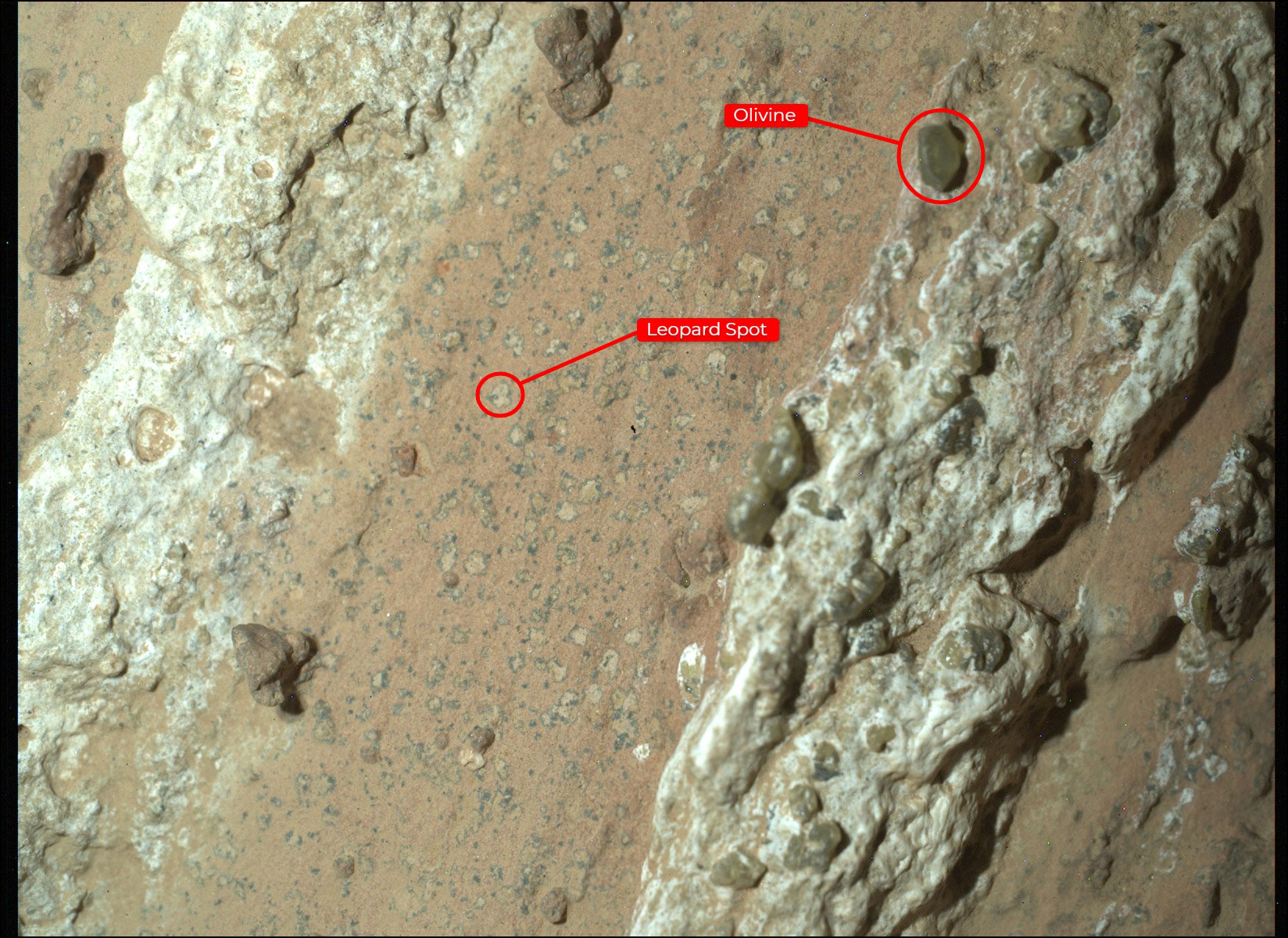
And the third is the tiny ‘Leopard spots’ seen dotted throughout the layer of reddish rock by Perservance’s PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry) instrument. Those irregularly-shaped, millimeter-sized spots are made up of lighter-colored rock surrounded by a dark border, basically composed of iron and phosphate.
The Significance of Iron and Phosphate
According to NASA, the presence of Iron and Phosphate is particularly significant because similar formations on Earth are often linked to microbial activity in oceans and coastal regions. On our planet, microorganisms reduce iron oxide, releasing iron and phosphate and leaving distinctive marks, aligned to those found in Cheyava Falls.
Ken Farley from the California Institute of Technology has highlighted that this discovery could represent our first clear evidence of organic material on Mars.
Volcanic Origins: A Competing Hypothesis
While the biological interpretation of Cheyava Falls is thrilling, there’s an alternative explanation. Organic molecules can also be formed through abiotic geochemical processes related to volcanic activity. The detection of Olivine crystals, a rock formed from the cooling of magma, suggests that past volcanic activity may have influenced its formation.

“We have our first compelling detection of organic material, distinctive colorful spots indicative of chemical reactions that microbial life could use as an energy source, and clear evidence that water- necessary for life- once passed through the rock. On the other hand, we have been unable to determine exactly how the rock formed and to what extent nearby rocks may have heated Cheyava Falls and contributed to these features,” Farley explained.
The presence of these green crystals within the rock raises the possibility that the intriguing characteristics of Cheyava Falls may not have been formed by biological processes. Rather, they could occur due to chemical reactions at very high temperatures linked to volcanic activity.
Seismic Insight: A Hidden Ocean Beneath Mars
Michael Manga at the University of California, Berkeley with Vashan Wright and Matthias Morzfeld from the University of California, San Diego conducted a recent research. The researchers investigated the presence of buried wanted by analyzing data collected by the InSight Lander, which explored the Martian interior from 2018-2022. The Insights’s SEIS instrument detected seismic waves reverberated throughout Mars, due to Marsquakes and meteor impacts.
“The speed at which seismic waves travel through the rocks of different densities depend on their composition, pore space, and what fills the pore space- either gas, water or ice,” Manga explained. By analyzing the differing arrival times of seismic waves from the same sources, Manga and his colleagues integrated these measurements with advanced rock physical models and probabilistic analysis, which enabled them to identify the combination of rock composition, water saturation, porosity, and pore shape within the Martian crust.
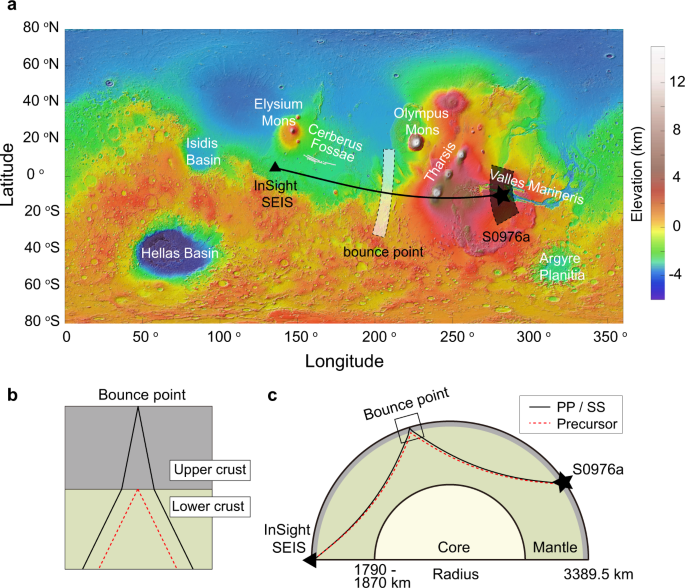
In conclusion, Manga states, “We have identified a substantial reservoir of liquid water. The data collected on Mars is most effectively explained by the presence of cracks in the mid-crust, which are filled with liquid water.”
An Innovative Era of Mars Exploration
The recent finding from NASA’s Perseverance rover marks a significant advancement in our quest to find life on Mars. The identification of Cheyava Falls, which exhibits potential microbial markers, along with evidence of extensive underground water reserves, paves the way for future explorations.
As Scientists eagerly await the future mission of Martian samples to return, these findings sustain our hope that we may one day uncover the definitive proof of life beyond Earth. Only by bringing Mars samples back to Earth and analyzing them with sophisticated laboratory instruments, we can conclusively uncover the origins of fascinating formations and organic compounds detected by Perseverance.
Whether through biological or abiotic processes, Mars continues to fascinate and challenge us, expanding the limitation of our knowledge and imagination. This new chapter in Mars exploration will enhance our knowledge of the red planet and deepen our quest to comprehend our place in the universe.
References:
1.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cheyava_Falls
2.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WafjeBSaAh4&list=WL&index=6
3.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-35662-y
4.https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2409983121
5.https://science.nasa.gov/resource/perseverance-finds-a-rock-with-leopard-spots/
6.https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/nasas-perseverance-rover-scientists-find-intriguing-mars-rock/
7.https://science.nasa.gov/resource/perseverances-selfie-with-cheyava-falls/
8.https://science.nasa.gov/planetary-science/programs/mars-exploration/science-goals/
Also Read: Europa Clipper has begun epic journey to find how Habitable Europa is!

Krishna Kumar Mahato is a physics graduate from Nepal, passionate about space exploration, quantum computing, and uncovering the universe’s mysteries. With certifications from NASA and Google, he provides scientific insight with engaging storytelling to explore humanity’s future in space.
