If you find the abilities of Doctor Octopus interesting, then there’s promising news: that reality is closer than you might think. Imagine a world where individuals like the character Doc Ock from Spider-Man can control prosthetic limbs effortlessly with their minds. What if your forgotten memories can be accessed naturally or learning a new language becomes as easy as downloading an app? Once confined to fiction, this futuristic concept can become achievable with advancements like Neuralink’s Brain-Computer interface.
Our brains are like natural electronic devices. Every move we make, every thought we have, is powered by electrical signals coursing through our nerves. When you move your arm to the right, specific sets of neurons are activated in a particular pattern. By using neuro-electrophysiological recording, a process that measures the electrical activity of neurons, we can quickly predict the direction in which the arm will move.
By using electrodes, we can capture and transmit these signals, which theoretically have the potential to enhance or restore brain function. This is the fundamental idea behind a brain-computer interface (BCI): a system that allows a person to control an external device using brain signals.
One of the most anticipated breakthroughs in Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) comes from a company known as ‘Neuralink.’ Founded in 2016 by the visionary billionaire Elon Musk, Neuralink’s mission is to pioneer implantable chips within the human skull that will enable the user to control devices and help people with severe motor impairments seamlessly.
Musk has famously expressed concerns about the potential dangers of uncontrolled artificial intelligence. He stated that merging with AI through technologies like Neuralink is crucial for humans to remain relevant and avoid being surpassed by artificial intelligence. However, what exactly is the technology that Neuralink has initiated human trials on, why is it noteworthy, and what ethical considerations does it entail? All of these questions will be addressed in this article.

Company’s Progress
In the initial stages, Neuralink focused on designing and testing electrodes that could record and stimulate brain activity. Over the years, they tested their devices through surgical implantation in various animals, such as monkeys and pigs. In April 2021, Neuralink displayed a significant advancement when a monkey demonstrated the ability to play the game “Pong” using the Neuralink implant. This breakthrough highlighted the potential for direct neural control of external devices.
Fast forward to May 2023, Neuralink achieved a major milestone as it received approval for human trials in the United States. Following this approval, in September 2023, the company initiated its first human trials, focusing on individuals with quadriplegia due to cervical spinal cord injury or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
On January 29, 2024, Elon Musk made an exciting announcement about a significant breakthrough. They successfully implanted a device in a human participant, marking a significant milestone. Musk expressed his optimism in a tweet, mentioning that the patient is recovering well and the results indicate promising neuron spike detection.

A Look at Neuralink Brain Chip Technology
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have been around since the 1990s, and now several companies are developing their own versions. Two major competitors for Neuralink are ‘Synchron’ and ‘Blackrock Neurotech’. The New York-based company Synchron is focused on developing an endovascular BCI device that can access every part of the brain using the blood vessels. On the other hand, ‘Emotiv’ offers removable EEG headsets that enable users to control virtual objects and interfaces through brainwave patterns and averaged signals produced by populations of neurons.
However, what sets Neuralink’s N1 implant apart and makes it unique is that, unlike others, their device is implanted directly inside the skull. This allows the electrodes to touch the brain surface directly, enabling the device to target the activity of individual neurons. According to neuroscientists, this level of precision is necessary for sophisticated thought decoding. Additionally, the N1 implant is completely wireless, offering greater flexibility and convenience for users. This has never been done before, and scientists are eagerly anticipating its real-world usage.
Neuralink calls its device the N1-Chip, which is comprised of a probe. The probe, made primarily of polyimide (a biocompatible material) with a thin gold or platinum conductor, is inserted into the brain using an automated process carried out by a surgical robot. Designed specifically to insert multiple flexible probes rapidly and precisely into the brain, minimizing tissue damage.
Each probe has a wire section containing electrodes that can detect electrical signals in the brain, as well as a sensory area where the wire connects with an electronic system for amplifying and capturing the brain signal. While current technology limits the device to recording groups of neurons rather than individual ones, Neuralink’s ultimate goal is to decode neural information into a binary code, enabling a deeper understanding of brain function and the potential to stimulate neurons for therapeutic purposes.
Significance and Applications
But you might be wondering, how does all this fancy technology make a difference in our everyday lives? Well, beyond just being a marvel of engineering, Neuralink can change lives and reshape how we interact with the world around us.
It has an obvious application – to assist individuals with severe motor impairments in communicating and operating devices using their thoughts. This has the potential to significantly impact the lives of people with conditions like paralysis, granting them a newfound sense of independence and control over their surroundings.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 15% of the global population (around 1.3 billion people) is affected by some kind of disability, with 2-4% experiencing significant challenges in their daily functioning (WHO, 2011). If Neuralink completes its human trials, it could significantly improve the lives of many individuals.
Neuralink is already envisioning its device to enhance human cognitive abilities, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving. A member of the visual neuroscience team at Neuralink shared that this project could offer a groundbreaking solution for individuals with retinal injury or blindness caused by eye trauma.
The essential plan involves directly connecting a camera to the visual cortex and using several thousands of electrodes to generate a visual image. In the future, this can potentially lead to superhuman vision, seeing the world in various wavelengths like ultraviolet or infrared light and radar. Cognitive disorders like dementia and blindness can be easily dealt with.
There is still a lot of uncertainty about how practical these applications are at the current stage of technological development. However, even if these advancements are difficult to achieve, Neuralink can still be incredibly valuable for studying the brain’s neural activity. This research has the potential to reveal important insights into consciousness and cognition.
“The side effect of this device is, you’ll end up learning a ton about how the brain works,” said one of the team members.
Understanding Concerns and Public Perception
While we should remain optimistic for a futuristic world, the possibilities mentioned above are still miles down the road, even over the next hill. The initial human trials ‘prime study’ is expected to last around six years, and the FDA will closely monitor the progress to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and guidelines. Furthermore, several factors could potentially impact the realization of these possibilities, such as ethical considerations, regulatory approvals, and societal acceptance.
Firstly, one of the major problems with Neuralink is the lack of published data supporting its technology. Even though they have conducted various experiments and worked on perfecting the design of the chip, much of the detailed data and results from these efforts have not been made publicly available in peer-reviewed journals.
During a conversation with CBC News, Dr Judy Illes, an expert in neurology, expressed that the lack of transparency equates to a lack of scientific rigor at this point. Secondly, the public is concerned about Elon Musk’s ability to effectively safeguard sensitive data obtained from participants in clinical trials, given Twitter’s previous mishandling of data and breach of their commitment to protect user rights.
The company has also faced scrutiny and controversy over alleged animal cruelty, including accusations of violating the federal Animal Welfare Act. Reuters reported that over 1,500 animals have died during Neuralink’s experiments since its beginning in 2018. There are also reports of a large number of primates being euthanized after undergoing medical trials. According to employees, Musk exerted significant pressure on the staff to expedite animal trials, potentially leading to flawed experiments.
The FDA rejected the application for human trials a few times before granting the green light for limited human testing under strict conditions. One major concern was the surgical process involved in implanting the chip. While the implant itself is small, the procedure still entails brain surgery, raising concerns about potential complications such as bleeding, infection, and damage to brain tissue over time.
Moreover, there is concern about the possibility of the device interfering with the brain’s natural signaling patterns and the potential risk of components migrating to other areas of the brain.
Public opinion of Neuralink varies greatly, reflecting different views on the potential benefits and ethical implications of brain-computer interface technology. Some people are skeptical, pointing to Elon Musk’s history of making grand promises and not delivering on time. For example, a Reddit user named ‘Amazing_Ad7386’ commented, “Elon’s companies have a poor track record of overpromising (especially in delivery time) and underdelivering.”
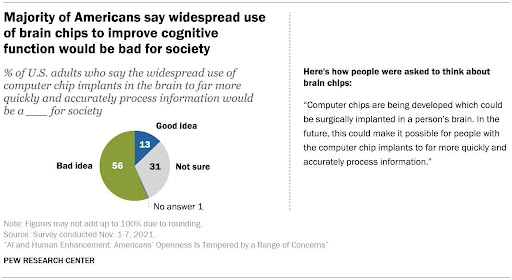
Similarly, a 2021 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found that Americans are divided on the widespread use of brain chips. While 63% expressed concerns, viewing it as “meddling with nature” and crossing moral boundaries, 35% embraced the idea as a way to advance humanity.
A Twitter user named ‘Stormrobinson’ expressed similar opinions, saying, “It’s a true feat of engineering and monumental human achievement — but there’s no way I’m letting someone drill a hole in my head to install a computer. I’ll probably have to pay a monthly fee to use.”
These responses highlight the complex ethical, societal, and practical considerations surrounding Neuralink’s technology and its integration into everyday life. As discussions continue, it will be essential to address public concerns and promote transparency in order to foster wider acceptance and understanding of brain-computer interfaces.
Ultimately, the future of Neuralink holds immense potential in advancing neuroscience and human augmentation, offering hope for a future where technology enhances our lives while respecting our values and ethics.
- References:
- Drew, L. (2024). Elon Musk’s Neuralink brain chip: what scientists think of first human trial. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00304-4
- Neuralink. In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuralink
- Sagar, R. (2020, September 19). Ten mind-bending applications of Neuralink, according to the team. Analytics India Magazine. https://analyticsindiamag.com/mind-bending-applications-neuralink-event/
- What is Elon Musk’s Neuralink brain chip, now being tested on humans? Al Jazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/1/31/what-is-elon-musks-neuralink-brain-chip-now-being-tested-on-humans
- Torrella, K. (2022, December 11). The Elon Musk Neuralink animal cruelty allegations, explained. Vox. https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/2022/12/11/23500157/neuralink-animal-testing-elon-musk-usda-probe
- UN World Health Organization (WHO), World Report on Disability: Summary, WHO/NMH/VIP/11.01, 2011, https://www.refworld.org/reference/annualreport/who/2011/en/89207
Similar Posts: Neuralink: One Microchip Fulfilling Hundreds of Possibilities

Aly Muhammad Gajani holds a Master’s degree in Space Science and Technology, specializing in Astrophysics together with GIS applications. His research focuses on galaxy evolution, astrophysical cosmology, exoplanet detection, and computational astronomy.

