Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the scientific discovery process by enabling the combination of data and theory to derive meaningful and accurate models of natural phenomena. One powerful approach to this integration is AI-Descartes, a method that combines logical reasoning with symbolic regression. By leveraging the strengths of both techniques, AI-Descartes allows scientists to derive scientific laws and formulas that are not only empirically accurate but also consistent with prior knowledge expressed through logical axioms.
René Descartes: A Renaissance Man
René Descartes, a prominent figure of the Renaissance, made significant contributions to philosophy, mathematics, and science. He possessed many skills and knowledge, making him a true polymath. Descartes’ philosophy placed great importance on rationality and logical reasoning, which laid the foundation for his famous statement, “I think, therefore I am.”
During the 17th century in France, Descartes played a crucial role in developing artificial intelligence by introducing the concept of dualism. According to Descartes, the mind and body are separate entities that are interconnected. He believed it was possible to mentally separate these “substances,” such as the mind, from the physical body. This idea was instrumental in shaping the notion of a machine mind distinct from its physical form, a key concept in AI.
Descartes also viewed animals as “automata,” or self-moving machines, following predetermined instructions like programmed machines do today. He applied his theories practically by improving clock designs and constructing robot-like machines, effectively bridging the gap between philosophy and technology. This foresight demonstrated his understanding of the potential relationship between humans and machines.
By leveraging the strengths of both techniques, AI-Descartes allows scientists to derive scientific laws and formulas that are not only empirically accurate but also consistent with prior knowledge expressed through logical axioms.
The Power of Symbolic Regression
Artificial neural networks (NN) and statistical regression are commonly used to discover patterns and relationships in data. Neural networks provide “black-box” models focusing on prediction, while regression models require a predetermined functional form and concentrate on parameter fitting.
Symbolic regression (SR) offers a different approach by allowing the functional form to be composed from a given set of operators and calculated from the data. SR models are often more interpretable than NN models and require less data, making them suitable for discovering laws of nature from experimental data.
The Challenge of Model Derivability
While SR can generate models that fit the data, identifying scientifically meaningful models consistent with prior knowledge is the challenge. Previous approaches have focused on balancing accuracy and complexity, but they must guarantee consistency with known background theories.
The problem becomes more complicated when logical axioms are involved, and automated theorem provers need help to generate theorems consistent with experimental data from a set of known assumptions.
Introducing AI-Descartes: Combining Reasoning and Symbolic Regression
AI-Descartes has been developed to address the challenge of derivable scientific discovery. AI-Descartes combines logical reasoning with symbolic regression to enable principled derivations of models of natural phenomena from axiomatic knowledge and experimental data. This approach integrates statistical and symbolic AI techniques to synthesize models that are both data-driven and based on first principles.
The Discovery Process
The AI-Descartes system follows a discovery cycle inspired by Descartes’ scientific method. Rather than starting with hypotheses derived from theory and testing them against data, AI-Descartes generates and assesses them against known background theories. The system consists of two main modules: the symbolic regression (SR) and reasoning modules.
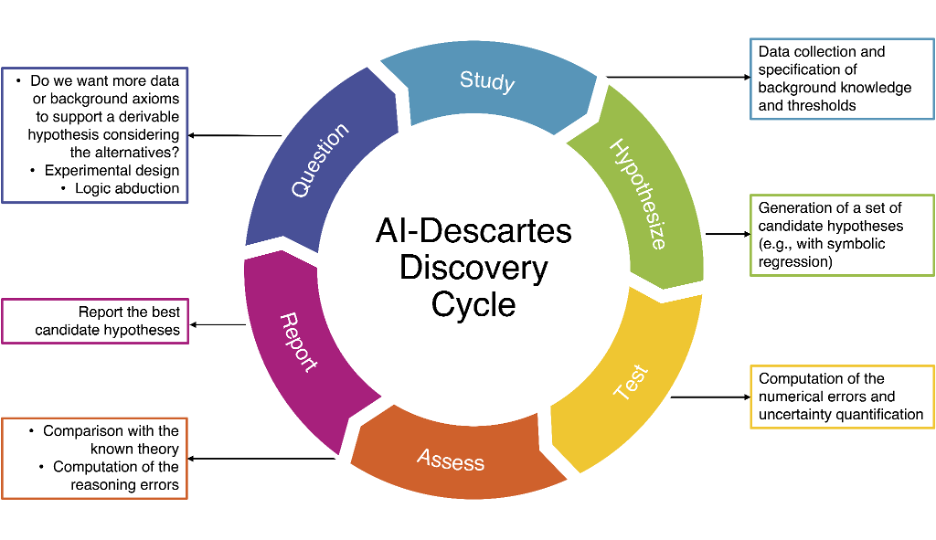
The SR module takes as input a set of operators, a grammar, and constraints on the functional form. It uses mixed integer nonlinear programming to find an expression that minimizes the least-square error between the model and the data. The SR module outputs a set of candidate formulas that fit the data but may not be derivable from the background theory.
The reasoning module is responsible for assessing the derivability of the candidate formulas. It takes the background theory and the candidate formulas as input and uses automated theorem provers and deductive reasoning to determine whether a formula is derivable. If a formula is derivable, it is returned as the chosen model for prediction. If none of the candidate formulas are derivable, the reasoning module provides a quality assessment based on the distance between the formulas and the background theory.
Experimental Validation
The AI-Descartes system has been tested on three problems to validate its capabilities.
- The first problem involves deriving Kepler’s third law of planetary motion from solar system data and background theory. The system rediscovered Kepler’s third law, demonstrating its ability to extract meaningful formulas from data and logical reasoning.
- The second problem focuses on Einstein’s relativistic time-dilation formula. While the system did not recover the formula from the data, it helped identify the formula that best generalizes it. The system could determine the theory that better explains the phenomenon by analyzing the reasoning errors with different sets of axioms.
- The third problem involves Langmuir’s adsorption theory, which includes material-dependent coefficients. The system used existential quantification to logically prove one of the extracted formulas by relating the SR-generated models’ coefficients to the background theory coefficients.
Industry Insights
AI-Descartes possesses a distinct advantage when it comes to handling intricate real-world data. While typical models, such as symbolic regression programs, tend to become overwhelmed by the minutiae, attempting to account for every minor alteration, AI-Descartes effortlessly sifts through the chaos.
It is akin to discovering the melody in a noisy room – this AI model hones in on the crucial patterns concealed within the data. The result? Models that are more transparent and dependable avoid excessive analysis and accurately reflect the occurrences within the data.
Tyler Josephson, co-author of the study and an assistant professor at UMBC, clarifies, “In this work, we relied on human experts to formalize the axioms of the background theory in a computer-readable format. If any axioms were missed or incorrect, it would hinder the system’s functionality.”
This implies that the experts translated the fundamental assumptions or principles of the theory into a format that the AI system could comprehend. Any errors during this process could limit the effectiveness of the system. Josephson adds, “In the future, we aim to automate this process, allowing us to expand our exploration to various domains of science and engineering.”
Conclusion
AI-Descartes demonstrates the value of combining logical reasoning with symbolic regression to obtain meaningful models of physical phenomena. By integrating data and theory, AI-Descartes synthesizes models that are both data-driven and based on first principles. This approach could revolutionize the scientific discovery process by accelerating the discovery of models consistent with prior knowledge. AI-Descartes is an accessible and knowledgeable guide, helping researchers uncover meaningful scientific insights from their data.
References:
- IBM Research Blog. (n.d.). AI Descartes: A New Era of Scientific Discovery. Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://research.ibm.com/blog/ai-descartes-scientific-discovery
- A History of AI. (n.d.). Descartes and the Dawn of AI. Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://ahistoryofai.com/descartes-2/
- AI Descartes. (n.d.). AI Descartes: Combining Data and Theory for Derivable Scientific Discovery. Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://ai-descartes.github.io
- SciTechDaily. (n.d.). AI Descartes: A Scientific Renaissance in the World of Artificial Intelligence. Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://scitechdaily.com/ai-descartes-a-scientific-renaissance-in-the-world-of-artificial-intelligence/
- Philosophy of Life. (2023). Introduction to the Special Issue on AI Descartes. Journal of Philosophy of Life, 2023(SI). Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://www.philosophyoflife.org/jpl2023si_intro.pdf
- Springer Nature Protocols and Methods Community. (n.d.). AI Descartes: Combining Data and Theory for Derivable Scientific Discovery. Retrieved July 17, 2023, from https://protocolsmethods.springernature.com/posts/ai-descartes-combining-data-and-theory-for-derivable-scientific-discovery
Also Read: HIPPOCRATES VS PASTEUR: IS MODERN MEDICINE AN UPGRADE?

Mohsin Iqbal is a student of Computer Science. His research interests revolve around Deep Learning, Medical Image Analysis using AI, and Large Language Models. With an unwavering commitment to spreading knowledge, Mohsin embodies his manifesto: benefit humanity through the power of Data Science and AI.

