The term “Deepfake” was first coined when a Reddit user with the same name shared a few digitally engineered adult videos of a couple of female celebrities in 2017; he used deep learning technique for the alternation.
Deepfake, one of the novel forms of misinformation, has become a real challenge in the modern communication environment due to its rapid spread through online news and social media.
Falsehood, fantasy, fake news all have walked along with the development of modern communication and journalism. There is evidence of misinformation since the Roman Empire (Barkhart, 2017). It was later developed as a strategy with the invention of print in the 15th century. The possibility of disseminating written misguided information in a faster way made the circulation of fake news much more accessible.
One of the remarkable examples of misinformation of our time was the radio broadcast of the “War of the Worlds” directed by Oscar Welles on Oct 30, 1928. This radio show was followed by thousands of listeners, and a minority believed that our planet is under the aliens’ attack, thanks to the fabulous narration of Welles.
The misinformation has been using against enemies in conflicts and wars, as we witnessed in World War I & II, Vietnam War, and the Gulf crisis. A recent example of fake news propaganda was of China and the US against each other. After the emergence of Coronavirus from Wuhan, the irresponsible statements/ tweets of former US President Donald Trump added fuel to the fire.
There have been different proposals for classifying fake news during the last few years, like news satire, a prevalent form of fake news with a significant presence in magazines, websites, and radio or TV shows. And news parody, which shares some of the characteristics of news satire, but is not based on topical issues.
The promoters of these pieces mostly try to deceive by blending them among the truthful ones. Like the spread of Coronavirus first linked to 5G network and then claimed that it was engineered by Bill Gates. It was told to the public that they can detect the virus-germ by placing a halved onion in their rooms and vice versa. The wave of misinformation and myths was so intense that WHO introduced a new term, “infodemics”.
Danielle Citron, a Prof of law at the Boston University, says, “it appears that the deepfake technology is being weaponized against women mostly for the revenge.”
The fake news conspiracy theories/ stories trend is not new; they have always been there, but in recent years, corresponding to the rise of social media, the public’s interest in fake news has grown sharply because “Controversy sells”.
Presently, one out of five internet users gets their information via YouTube, Facebook, or Twitter. We live in a post-truth era characterized by the digital information warfare running by the media giants to manipulate public opinion for their personal interests.
Besides, photo manipulation, alteration of images, and more recently, videos are widely used to build a different reality for advertising and public relations. In Nov 2019, Hao Li, pioneer of deepfake, stated that “this trend is growing more rapidly as I was expected. Soon it’s going to get to the point where there is no way that we could actually detect deepfakes anymore, so we have to look to new technologies for the solution.”
Hao’s AI firm Deepfake found over 15,000 fake videos online in Sep 2019, nearly doubled in just nine months. A staggering 96% were pornographic, and 99% of those mapped female celebrities’ faces onto porn stars. Danielle Citron, a Prof of law at the Boston University, says, “it appears that the deepfake technology is being weaponized against women mostly for the revenge.”
The fraud through deepfake audios, voice skins, and voice clones is also trending. Last March, the Chief of the UK subsidiary of a German energy firm paid nearly 2 00,000$ into a Hungarian bank account after being phoned by a fraudster who mimicked the German CEO’s voice. Similar scams have reportedly been used in recorded WhatsApp voice messages.
How are Deepfakes created?
Hyper-realistic or deepfake videos are the product of Artificial Intelligence applications that can combine, merge, replace, and superimpose images or short video clips for creating a fake video that appears authentic. The game-changing factor of deepfakes is the scope, scale, and sophistication of the technologies involved in its creation process.
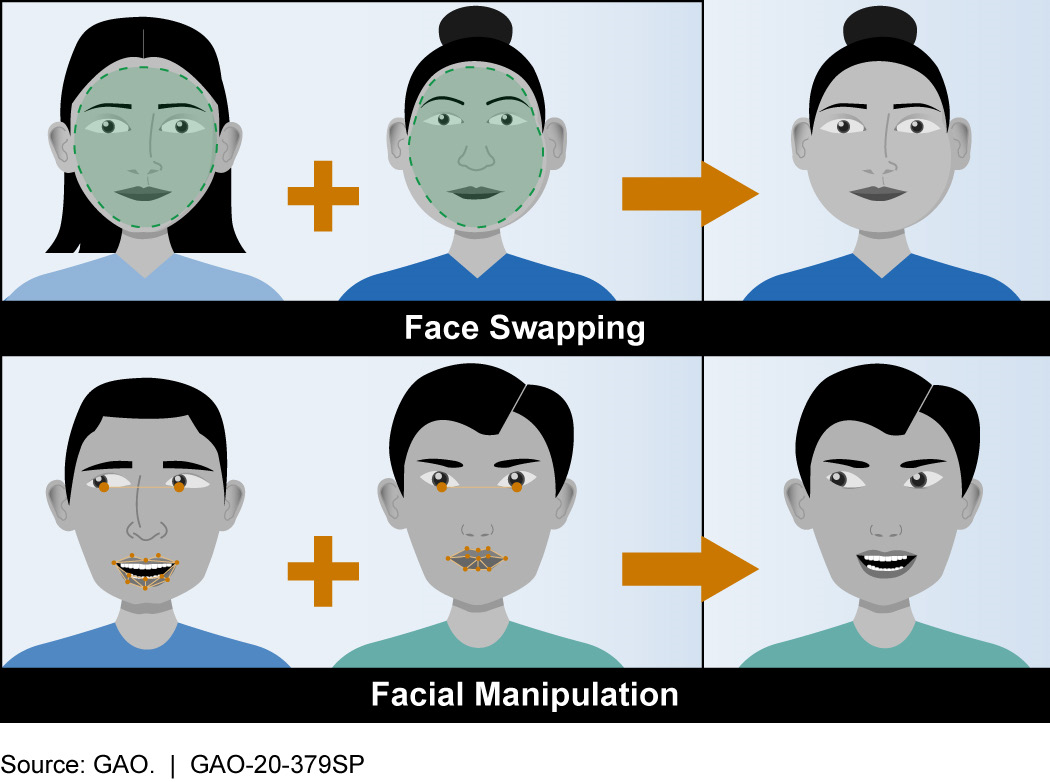
It takes a few steps to make a face-swap video. First, runs thousands of face shots of the two people through an AI algorithm called an encoder. The encoder finds and learns similarities between the two faces and reduces them to their shared standard features, compressing the images in the process. A second AI algorithm called a decoder is then taught to recover the faces from the compressed images.
Because the faces are different, one needs to train one decoder to recover the first person’s face and another decoder to recover the second person’s face. To perform the face swap, he simply feeds encoded images into the “wrong” decoder. For example, a compressed image of person A’s face is fed into the decoder trained on person B. The decoder then reconstructs the face of person B with the expressions and orientation of face A. For a convincing video, this has to be done on every frame.
How to spot Deepfakes?
One of the biggest challenges of deepfakes is to find out how to counteract them knowing that the debunking methods’ development is always late regarding the production of misinformation. However, a great deal of effort has been made—and is still under the attempt to develop technology-based tools for detecting and correcting it, both from public and private organizations.
Researchers from the Binghamton University, State University of New York, and Intel Corp have teamed up to develop a tool, “Deepfake catcher”, which boasts an accuracy rate above 90%. This tool works by analyzing the subtle differences in skin color caused by the human heartbeat. In deepfake, there is no consistency for the heartbeat and no pulse information at all.
Another remarkable effort is the US’ Deepfake Detection Challenge (DFDC), co-partnered by AWS, Facebook, and AI’s media integrity steering committee US, to spur the researchers around the globe to build innovative technologies that can help detect manipulative media.
There are specific rules one can follow to detect a deepfake video, such as facial transformation; checking if the eye is blinking as humanly as possible (weakness which has now been fixed in new videos), watching the eyes, scanning the cheek and forehead movements, etc. told Asad Makki, senior business solution manager at SAS.
This is how a layperson can detect manipulation in online content, but high-quality deepfakes aren’t easy to discern. The only way left is to educate and stay updated about advancements, both in deepfake tactics and detection technologies. Besides, one needs to build intuition for identifying “what is real and what is fake”.
References:
- https://deepfakedetectionchallenge.ai/
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2020/jan/13/what-are-deepfakes-and-how-can-you-spot-them
- https://www.cogitatiopress.com/mediaandcommunication/article/view/3494

Saadeqa Khan is the founder, CEO, & Editor-in-Chief of Scientia Pakistan. She’s a member of the Oxford Climate Journalism Network (Second Cohort) and NASW. Saadeqa is a fellow of NPF Washington, The Falling Walls Foundation, and the Science Journalism Forum. Saadeqa has won several international journalism grants and awards for her reports.

