Exoplanets are possible worlds like our planetary system orbiting around any other star than our Sun. NASA’s quest for exoplanets has achieved several milestones in the past three decades. Till now, more than 4324 planets have been discovered and are present in NASA’s exoplanet catalog.
More than 200 exoplanets have been explored in the year 2020 with a couple of breakthroughs in exoplanets to find intelligent life with empathy and knowledge. The eyes are still on other solar systems in quest of the possibility of other Earth-like worlds where life can be present in any form. Some exoplanets are of different sizes, properties, specifications, masses, and composition.
There are gas giants, and rocky planets roaming around a star or even roaming freely around the galactic center unbounded to any star and are known as rogue planets. The exoplanets discovered until now are quite from a tiny region of our Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy is supposed to have more than 300 million, the potentially habitable world, out of ten of billions of exoplanets that may be able to harbor life.
Exoplanets space ventures
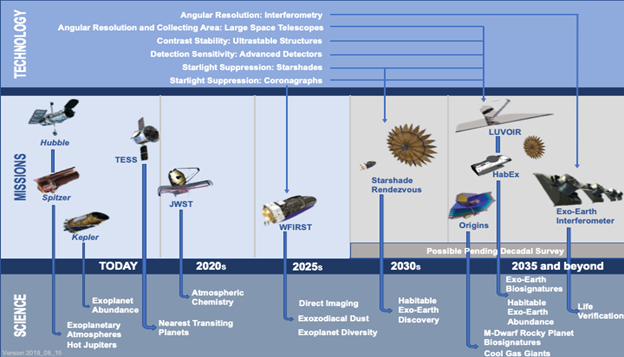
A couple of space missions carrying telescopes, satellites, probes have been sent by NASA for the exploration and discovery of exoplanets, and there are more advanced telescopes like James Webb Space Telescope & Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, which are planned to be sent this year on October 31, 2021, & 2025 respectively. Now we know because of the previously done discoveries by telescopes like Hubble, Kepler. Spitzer & TESS that there are more planets than stars in the galaxy, and there is more than 50% chance that the planetary system of Sun-like stars has the planetary system that does support life like our very own Earth. Kepler Telescope, also known as “Planets Hunter,” has exponentially discovered exoplanets in its nine-year expedition. Though by today’s date, Earth is the only life-supporting planet in the whole known Universe.
Astrobiology: Quest for intelligence life
Astrobiology has been developed to read any intelligent life signs in our planetary system or far across the ocean of planets in our galaxy and moreover in our Universe. There may be life lying beneath the surface of water or ice, there may exist breathing organisms in rocky planets, or there may be a living creature in planets abundant with elements present on our Earth. Life could be in any form, shape, size, or composition that we may have never seen or our mind has never predicted before.
They may be the species capable of fundamental change, and their DNA may be determining their fate in a much-hidden way veiled through the other world. There may be unfortunate life perished from the face of their planets, or there may be any species completely wiped by any other species. There is also a chance that somewhere on any other planet, life may be flourishing in any form at the micro-level, give birth to an intelligent life millennium centuries after. Human exploration has now been open to the imagination with dynamics more than before to think beyond limitations.
Earth: Story of the evolution of only life-supporting planet known in the Universe
Earth was born in fire, formed from a dead star; in its beginning time, it was like a firing ball spinning very faster with shorter days just to 6 hours long. Moon was 10 times more near our young planet with greater gravitational pull and thousand times high tidal waves the world has ever known. Earth was not a place to foster human life or any other kind of life back then.
The atmosphere was hostile, mostly composed of carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia, in which life was impossible to exist in any form. But then millenniums of centuries after then, life was nurtured in the form of a tiny creature like shrugs of the methane eating carbon dioxide in sunlight found a way to make a living in the oceans and crafted the whole world that we know today. These first autotrophic bacteria, very similar to the cyanobacteria, enriched the Earth with oxygen eating up carbon dioxide and giving oxygen, which destroyed the methane shrouds, turning the skies blue and cool.
The ozone was formed from the high up oxygen atoms creating an invisible canopy against harmful radiations of the Sun. Hence the life sprouts out of the oceans to face the new opportunities to flourish in variant sizes, shapes, and compositions to step on the ground as new inhabitants. Soon after, there were ears, eyes, feet, wings, fins, everywhere roaming in the kingdom of land and oceans, witnessing the very evolution of life. This is the exception rather than the rule and holds so many mysteries that the human mind cannot decipher yet.

Techniques that are opening the gateways to discovering different kinds of exoplanets
So when we place our vision beyond the horizon, we look deeper into the infinite possibilities. We have changed our insight as well as our tools with time. We have discovered thousands of planets by now, and the count will rise to tens or hundreds of thousands within the next decade. We are counting on more powerful observing robotic telescopes mounted in space to tell us our past and future in a different way. We are developing new methods of identifying and detecting rather than just catering to them through direct imaging.
We have discovered 3287 exoplanets through transit method, 826 exoplanets through radial velocity method, 51 exoplanets through direct imaging, 106 exoplanets through gravitational microlensing, and one planet through astrometry. The researchers have categorized them according to their masses and sizes, and they have calculated their temperatures. We have the simulation for the predictability of the light level, sky color, and other specifications. So far, the discovered exoplanets have been divided into four major categories that include:
- Gas Giants
- Neptunian
- Super-Earth
- Terrestrial
Gas Giants
The large exoplanets are mostly composed of helium/hydrogen or Jupiter and Saturn of our planetary system. They may be far huge than Jupiter and much closer to their stars than anything found in our solar system. There are 1357 confirmed Gas Giants’ discoveries, with 51 Pegasi-b as one of the famous gas giants.
Neptunian
Those exoplanets that fall in Neptune or Uranus’s size category of their own planetary system are considered Neptunian exoplanets. They usually have hydrogen/helium abundant atmospheres with core and heavier metals. There are 1467 confirmed Neptunian exoplanets discovered until now, with Kepler 1655-b as one of the most helpful discoveries of this category.
Super-Earth
Super-Earth is gas or rock giants exoplanets that are massive than our Earth and lighter than Neptune. They can be double the size of Earth to ten times its mass. There have been 1331 confirmed Super-Earth discoveries in NASA’s catalog with Barnard’s Star-b as the 2ndclosest star to us until now.
Terrestrial
The exoplanets between half of Earth’s size to twice its radius are classified as Terrestrial exoplanets. They are highly expected to be with rocky surfaces and similar elements as found here. There have been 163 confirmed terrestrial exoplanets in the NASA catalog of exoplanets with Trappist 1-e as one of the most special discoveries of this class.

Best chances of life in exoplanets
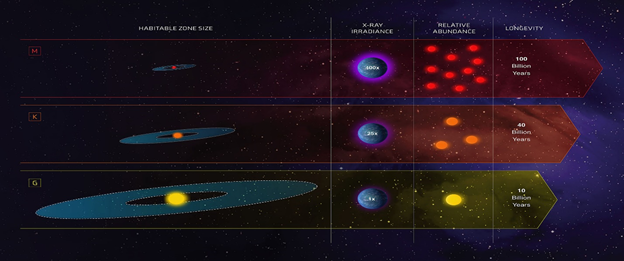
There are wide-ranging stars in our universe, with their specification impacting many factors, including their star system. This evaluates if their system can have the rocky planet in their orbit with the possibility of liquid water or any kind of life-supporting elements. There are huge complications in determining the potentially habitable planets. The scientist is more looking towards the exoplanets in the “Goldilocks zone” to their parent star, which varies with the star size and mass.
The habitable zone or “Goldilocks zone” is the region around any star where the temperature is just right enough to support life like our planet Earth in our solar system. The temperature is neither too hot nor too cold but moderate enough to support liquid water, which has been the key component as far as we think to harness life. There is a good occurrence rate of exoplanets’ possibility to be inhabitable zone predicted by the models created through the absorption of light by the planet given off by their star established on a star’s flux.
Possibilities of breakthroughs in future exploration
The human quest is continuously pulling its threads to make some real breakthroughs and answer our existence’s mysteries. We even don’t know how intelligent species like us find their way into this planet 480 million years back. We don’t know that from where our consciousness comes from that witnessed the evolution of life diversity in millions of other forms. We faced mass extinction and then sprouted again to witness another era of philosophical implications of life and understanding different patterns attached to it. We design the world and architect it as we wish, incarnating the destinies, choosing life, and developing our own patterns, facing chaos that unleashes in very mystical ways.
We inhabit a cosmos hidden in the veils of unrevealed dimensions of paradoxical realities that the human mind cannot understand. We own a single perception, but there may be paradoxes that are stopping us from decrypting them. Nature intimate secrets, and in stretching the fabric of space and time, there may be unfolded realities and anomalies that may be just a few steps away from knowing. The future holds too much that we don’t know today and what we don’t know never means that it does not exist. It may exist in a way beyond our understanding for now, but it will not be forever. The curtain will move, and the revelations will occur if not today, then tomorrow, and if not tomorrow, then the day after it, whenever it will, it will unleash the deepest secrets of nature.
References:
- https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
- https://science.nasa.gov/
- https://www.space.com/17738-exoplanets.html
- https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/universe/exoplanets/
- https://www.planetary.org/worlds/exoplanets
Also, Read: Teen discovers a new exoplanet

Hassaan Bin Zaki is a Space Science graduate, a passionate public speaker and an enthusiastic creative content writer. He is the Founding President of the Society of Astronomy and Space Technology (SAST). He is also the Project Lead of Rah-e-Qamar Pvt. Ltd. for Karachi Chapter which is a space-based private company. He holds a vision to evolve his country in making breakthroughs in the field of Space Science and Technology and to unleash the true potential of his country in front of the world in each and every field.

