While addressing weight loss, the keto diet is a popular candidate in the running. I believe many of us have heard an array of views such as “Keto is the best way to lose weight” or “You can consume any fats during a keto diet.” On the contrary, some claim “There is no science behind the diet” or “You will lose muscle mass during the keto diet.” To my utter dismay, all these claims are non-validated opinions that greatly impact our notion towards keto and diet in general. Unveiling the candor behind all the keto myths, the composition below all you need to know.
What is the explicit meaning of “Keto Diet”? The Keto diet is high fat and minimalistic carbohydrate diet. This diet’s prime motive is to highly reduce the carbohydrate content of the diet and replace it with healthy fat intake, which is then metabolized, thus acting as a major energy reservoir for the body. Generally, glucose is the major source of energy for the body obtained in the form of carbohydrates but, during keto, your body starts storing fats and proteins, which can cut off surplus calories via carbohydrates.
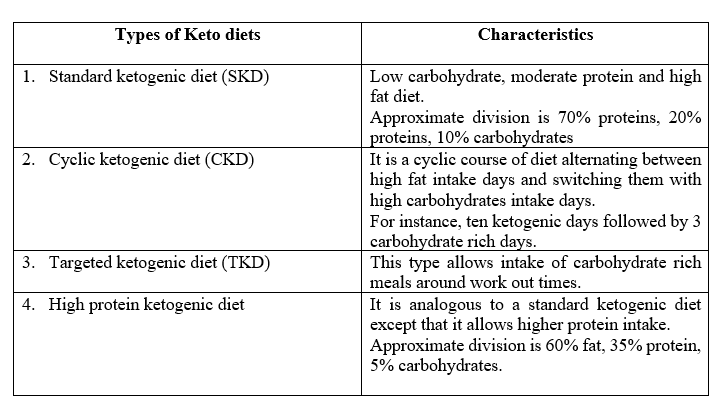
Moreover, the keto diet aids in maintaining insulin at homeostatic levels, which is once the body adapts to this change (a state of ketosis), it becomes proficient at fat burning, lowering down sugar levels in the blood, and producing ketones: an essential energy component for the brain. This helps the body retain muscle fat and prevent excessive fat uptake. On a basic level, there are four different types of diets under the keto diet umbrella. An insight into these contrasting subtypes is summarized in the table below.
Once an individual starts with this diet, he/she eventually enters a state of ketosis. To confirm the body’s switching to ketosis, blood, urine, and breath tests can be performed. Furthermore, there are some visible changes in body processes that confirm the keto diet’s positive effect on the body. These signs include enhanced thirst, drier mouth, increased urination, and loss of appetite.
Switching to a keto diet does not mean consuming all sorts of foods. An array of components such as meat, cottage cheese, avocados, fresh vegetables, seafood, eggs, and healthy oils(not overly processed and refined) can be consumed while following keto diet parameters. On the contrary, intake of flour, barley grains, fried items, and rice must be avoided.
The brighter side of Picture
Starting with the keto diet’s fruitful outcomes helps in weight loss by lowering the hunger-stimulating hormones, boosting metabolism, and lowering the appetite. In fact, review studies on animals and humans in 2017 showed that some individuals on the keto diet showed decreased total cholesterol levels. High cholesterol is one of the root causes of many cardiac diseases. Hence a decline in overall cholesterol levels in the body is an added benefit.
Furthermore, another 2019 review claimed that the keto diet might help strengthen and protect neuronal cells/brain as a whole, such as in Alzheimer’s disease. The Keto diet results in ketosis in the body. According to the epilepsy foundation, ketosis can decrease seizures in individuals facing epilepsy issues by reducing several epilepsy symptoms. Another interesting discovery was the positive role of the keto diet in helping cancer patients. High fat intake results in enhanced oxidative stress (a biological process that allows the body to destroy reactive and harmful species/molecules in the body) in cells that can potentially kill the tumor cells in a cancer patient.
Furthermore, a ketogenic diet stabilizes insulin levels and reduces blood sugar levels. In fact, this is beneficial for people suffering from insulin resistance and diabetes. It is believed that in some people, adaptation to a ketogenic diet results in a 50% reduction in insulin supplementation. However, the diabetic patient must consult thier doctor before following keto diet restrictions to ensure no further complications.
Metabolic symptoms are various symptoms, including high blood pressure, fasting blood sugar levels, abdominal obesity, and high cholesterol levels. Surprisingly, a low carb diet intake significantly reduces these symptoms’ expression to a level that these symptoms become nearly nonexistent.

Parkinson’s disease is a nervous system disorder characterized by low levels of a signaling molecule, dopamine. Lack of dopamine has adverse effects on the body and metabolic processes. However, the prevalence of ketosis in the body shows a promising treatment against Parkinson’s disease.
All that glitters is not gold!
Weight loss is the most common reason for individuals to follow the keto diet. It is not just a fancy name; it has several complications.
Within the initial days of following a keto diet, an individual experiences several changes called “Keto flu.” Keto flu is marked by dizziness, headache, weakness, irritability, nausea, increased urination, and vomiting. The change of substrate provided to the body (from carbohydrates to fats) also results in dehydration. With increased urination, the body loses a significant number of electrolytes, which intensify these symptoms. Generally, these symptoms last for around a week.
Loss of electrolytes makes the body more prone to kidney-related issues such as acute kidney injury or the prevalence of kidney stones. An affected individual might be at risk of cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeats).
Moreover, the keto diet demands the elimination of certain types of legumes, vegetables, and grains, which are considered beneficial for the body. Lack of availability of these essential food sources results in scarcity of particular vitamins and minerals whose depletion, in the long run, can be the cause of numerous chronic diseases.
Binge eating is another side effect of switching to the keto diet. Cutting carbohydrates in the diet stimulates the brain to release a chemical called neuro peptide-Y that signals the body for carbohydrate supplementation. If these conditions are not reversed, it amplifies the craving for carbohydrate-rich meals, posing a threat of eating disorders. Due to lack of fiber and carbohydrate consumption, Constipation is another candidate in the pool of complications one may face while being on keto leading to diarrhea.
One of the most unpleasant effects of the keto diet is bad odor. Ketones are produced as byproducts of ketosis. Acetone is a major component of ketone bodies, which is often removed from the body via exhalation. This causes bad breath as bacteria builds up in the mouth.
Yo-yo dieting is not uncommon with any low carb diet, particularly for a long term dieting regime. As the name suggests, the Yo-yo diet refers to inconsistency in maintaining the dietary restrictions by switching to normal eating habits then, which causes frequent loss and weight gain. Sticking to a specified diet for the long term is not a piece of cake. Sudden weight shedding and gaining can have adverse effects on health.
Be it any diet, consultation with a doctor or nutritionist is a must before following dietary restrictions. Each body reacts differently to a particular diet. Not everything works for everyone. The toughest part of the diet is not about what you eat; it is about what you see others eat. Refrain from opting for the best lifestyle in the world: chase the lifestyle best suited to your body and health.
“It’s not a diet, It’s a lifestyle.”
References
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ketogenic-diet-101#fa-qs.
- https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/forefront/health-and-wellness-articles/ketogenic-diet-what-are-the-risks#:~:text=The%20keto%20diet%20could%20cause,%2C%20liver%2C%20thyroid%20or%20gallbladder.
- https://www.health.com/weight-loss/keto-diet-side-effects
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/type-1-diabetes-guide/what-is-ketosis#1
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/15-conditions-benefit-ketogenic-diet#TOC_TITLE_HDR_9
Also Read: NERVE BLOCKS; THE POTENTIAL GAME-CHANGER FOR CHRONIC CANCER PAIN

Maira Masood is a BS Biosciences student at NUST, Pakistan. She aspires to be a geneticist and wants to play an active part in spreading scientific awareness through writings.

