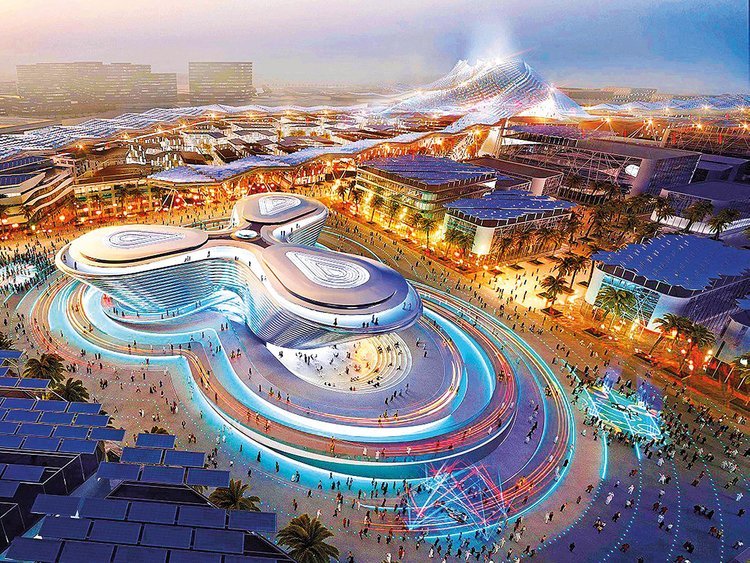
World Expo, officially known as “International Registered Exhibitions,” has been held every 5 years at different locations worldwide. Its history goes back to 1851 when first held at Crystal Palace, London, to showcase the Industrial revolution on a larger scale. It has been held in several western countries like Spain, Portugal, Germany, and Canada, to name a few. Japan was the first Asian country to host a World Expo in 1970. At these exhibitions, numerous mega structures came to light, like the world’s first Ferris wheel was installed at World Expo 1893 in Chicago. The world’s fastest elevator of its time, “The Atomium,” was also a part of World Expo 1958 in Brussels.
Since the pandemic’s start in November 2019, the world was forced to halt all its livelihood and resort back to the basics of life. Last year World Expo came to the Middle East as “Dubai Expo 2021”. It was scheduled to open in Oct 2020 but was postponed due to another wave of Coronavirus, which opened eventually in Oct 2021 and is ongoing till March 2022. As of February 2022, it successfully touched 15 million visitations bringing back the post-pandemic charm.
Connecting Minds, Creating the Future
With over 191 countries participating through their respective pavilions, this expo looks promising in providing a better future for subsequent generations. ”. World-class architects, designers, researchers, and immense talent came together to showcase their expertise to create this mega project. It is divided into three zones, Opportunity, Mobility, and Sustainability.
Several countries are participated in the Sustainability zone and display their futuristic technologies mainly for creating energy from recycled material. This pavilion generates its own power to run itself in electricity and water. Germany, UAE, Singapore, Netherlands are a few prominent names in this district.
Hungary and New Zealand are the prominent countries in the Mobility District in Dubai Expo 2020, along with Barbados, Turkmenistan, etc. Named as “Alif”, an Arabic alphabet is dedicated to mobility. With the eye-catching gallery, Alif is designed by British Architecture firm Foster+Partners. It has the world’s most giant elevator with a capacity of 160 people. From the early history of mobility to the present and the future, this pavilion is a marvelous piece of artwork.
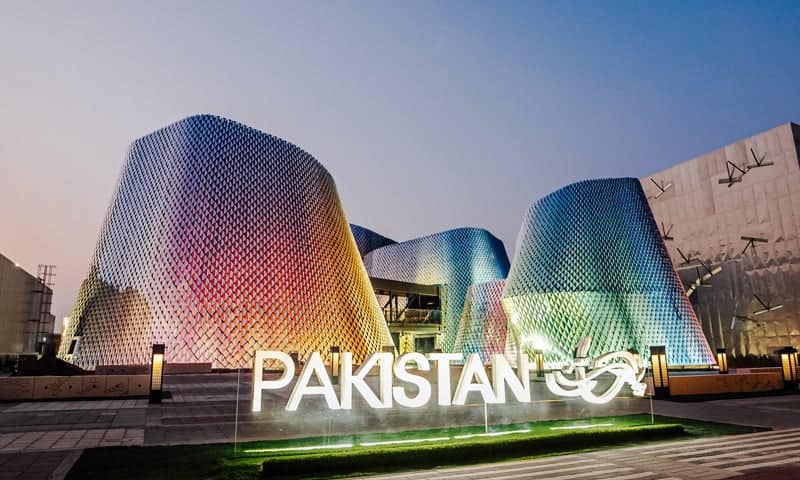
Several countries, including Pakistan, UAE, India, and Romania, are a part of the “Opportunity district” at Dubai Expo 2020. They displayed their respective cultures, history, and their present prospects. Countries have also shown their future goals in terms of technology and advancements. Going by the slogan “Mission Possible,” the opportunity pavilion brings together a place to connect billions of people, sharing their experiences and celebrating their uniqueness. AGI architects design it.
Pakistan
Pakistan has its pavilion in the opportunity district, presenting our culture, history, and heritage in a large-scale manner. Designed by Al Jabal Eng/Rashid Khan, it is recognized as one of the best pavilions. Based on the immersive and interactive concepts, Pakistan’s cultural diversity has been showcased in a very holistic manner. A history of 7000years has been shown with Pakistan’s present and future too. Handcrafted pieces from different artisans are put together in the form of a Bazaar where visitors can purchase them as a token of memory. Two dining facilities are also available at Pakistan’s pavilion “Dhaaba” and “Daawat”. Visitors can indulge in rich street food from Dhaaba, while Daawat provides all of the best Pakistani cuisines.

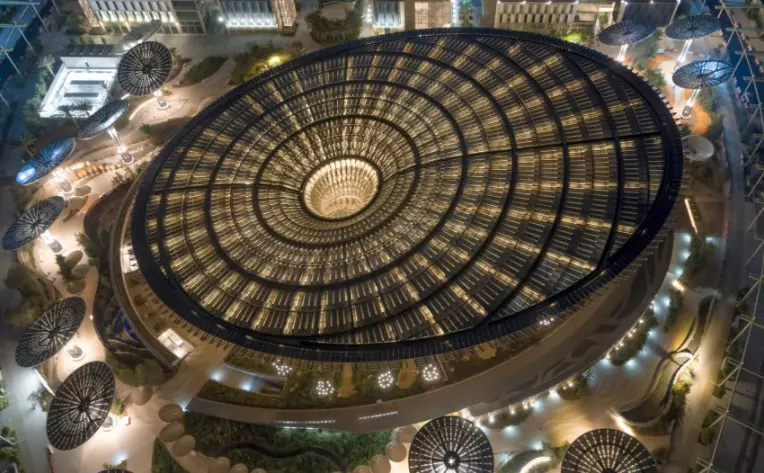
Terra: Sustainability Pavilion
The main building of this district is named “Terra”. It is designed by UK firm Grimshaw Architects. This 135m pavilion generates all its water and energy. This supertree is 97% made up of recycled steel to support 1055 solar panels. It is in a shape of a canopy to anchor the sustainability district.
Along with the solar panels, 18 auto-rotating energy trees surround it to generate 4gigawatt hours of electricity annually. This canopy collects stormwater and dew and smaller water trees, which are also placed around this structure.

Due to the ecological concerns and rapid increase in global warming, the world is forced to take several measures to increase the amount of energy and lower the ecologically harming aspects of carbon submissions. Wind, water, wood, and biofuels are the most widely used renewable energy sources globally. Still, with new technologies like green hydrogen marine solar, the future for more eco-friendly energy is bright.
Renewably produced hydrogen or GREEN HYDROGEN is the fastest-growing energy resource. Low emissions and lower value of electricity grids help decarbonize the industrial process. It can be blended in natural gas pipelines and can also be used to produce green ammonia, which is the primary source of fertilizers. It can bring a significant change in safekeeping our environment from several industrial hazards.
A few of the most widely recognized pavilions in this district are discussed below:
Netherlands
The Netherlands introduced a miniature climate system, “Biotope,” with the theme of “Uniting Water, Energy, and Food”. It has a cone-shaped vertical farm harvesting and cultivating water, energy, and food. Built by V8 Architects, it is made up of locally sourced materials. They developed a solar-powered rain shower, “Sun Glacier”, an innovation that allows producing hundreds of liters of water from dry air every day. This water is then used to produce edible food-like mushrooms, tomatoes, etc.
They have also published a book, “Raining Stories,” which is widely available for the public to read about all the technologies they have used in maintaining their pavilion in the desert region of the Middle East.
Germany
One of the most entertaining pavilions is designed by a firm Lava, facts and fiction in “Edutainment”. They created it in the campus-like form, further dividing it into three parts;
- The Energy Lab
- The Futuristic Lab
- Biodiversity Lab
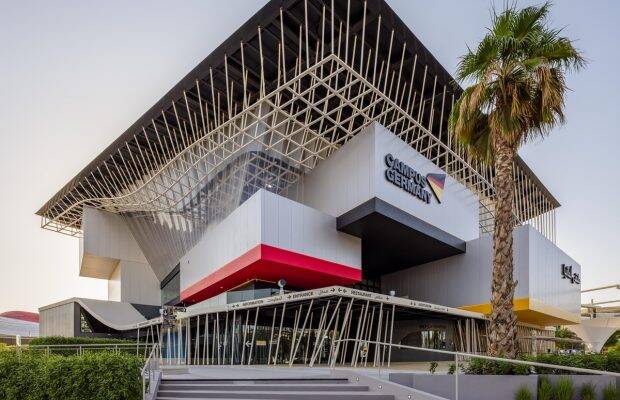

They displayed their energy revolution “Energiewende” in a detailed manner that aims to transit Germany into a low-carbon, environmentally sound, and affordable energy supply. From generating energy through the futuristic innovation of “EnerKite”, hydroelectricity, photovoltaics to preserving it in hydrogen storage and DeepSea storage, it is the most interactive exhibit in Dubai Expo.
Singapore
This multi-layered, three-story, 9-meter tall garden developed by “WOHA” architects operates on clean, renewable energy. It is a prototype of regenerative design that aims to repair and restore the ecosystem and biodiversity. With the slogan “Nature, Nurture and Future”, Around 517 solar panels generate electricity for this pavilion.
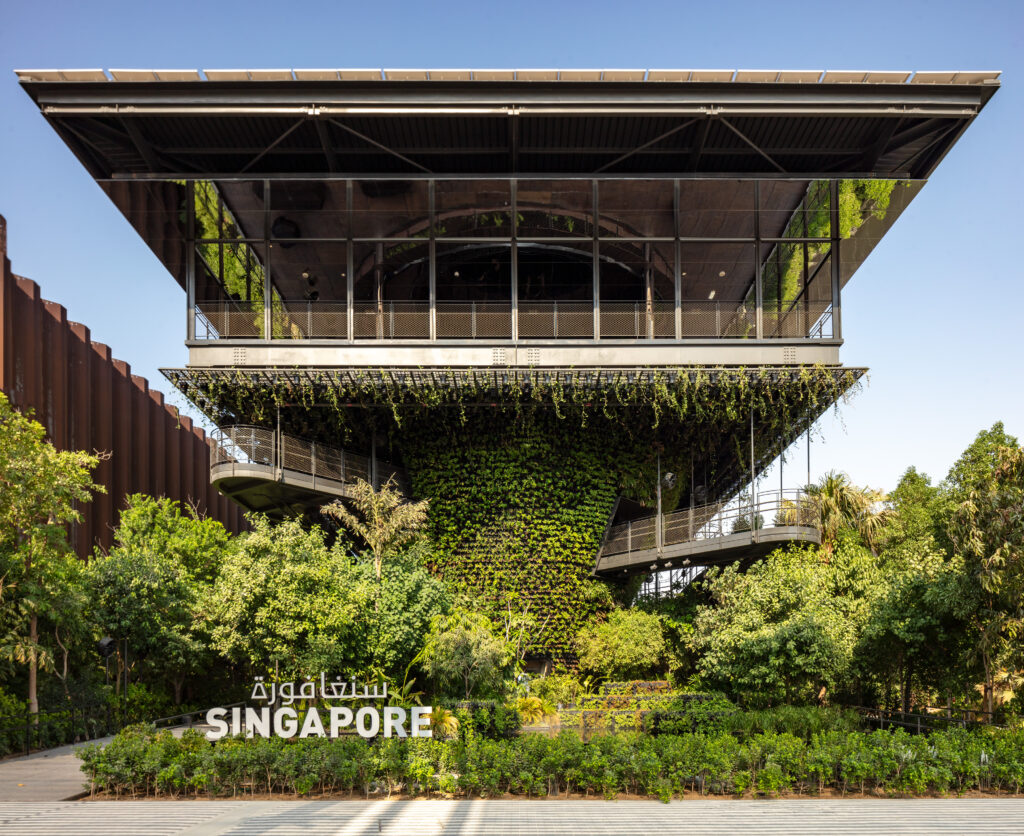

They introduced “EcoDigestor,” which converts food waste into recycled water on-site. To minimize energy-intensive water treatment pumps, they used plants to purify water streams naturally through the “Phytoremediation” method. Regenerative technology sets a net-zero target for its water and energy use.
Plenty more pavilions show human advancement and a wide range of diversity, ensuring our safe and healthy future. Dubai Expo is exhibiting the cultural aspects of the human race and the history and the future in a broader light.
References:
- https://www.expo2020germany.de/en/
- https://www.singapore2020expo.gov.sg/
- https://www.archdaily.com/search/all?q=netherlands%20pavilion&ad_s
ource=jv-header - https://www.dezeen.com/2021/10/15/grimshaw-sustainability-pavilion-
expo-2020-dubai-significant-unnecessary-emissions/ - https://pk.mashable.com/culture/12650/expo-dubai-2020-with-8-key-
spaces-pakistan-pavilion-offers-insight-into-countrys-hidden-treasures - https://www.luxuo.com/culture/events/dubai-2020-expo-living-
rainforests-augmented-reality-and-more.html - https://edition.cnn.com/travel/article/sustainability-pavilion-expo-2020-
water-energy-dubai-spc-intl/index.html - https://virtualexpodubai.com/sustainability-district
- https://www.expo2020dubai.com/en/understanding-
expo/participants/country-pavilions/pakistan
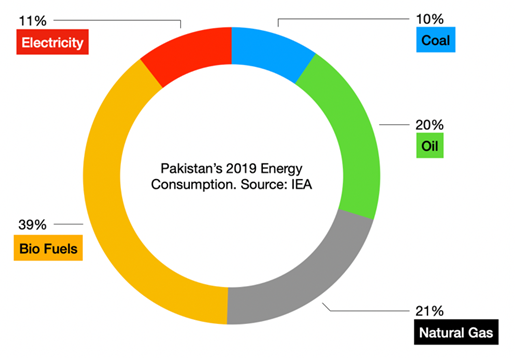
Also, Read: Energy Crisis in Pakistan— Electricity Transmission and Distribution Analysis