Earth, a habitable planet that supports millions of lives, is what we all have in common. Doubtlessly, this planet is a blessing worth fighting for. However, the rate at which we are deteriorating Earth is an eye-opener. Though the figures may not sound highly deleterious, in reality, we are destroying our planet faster than we can process. Even though we claim to be advanced enough to be stepping into the 21st century and producing innovative ideas and solutions to facilitate humankind, we need to focus on grassroots and protect our environment first.
“What’s the use of a fine house if you haven’t got a tolerable planet to put it on.” – Henry David Thoreau
Statistics reveal astonishing facts about environmental degradation. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change is estimated to cause 250,000 added multifactorial deaths per year due to malaria, malnutrition, diarrhea, and heat stress between 2030 and 2050. 7,000,000 casualties have occurred due to air pollution, as stated by WHO (2016). Radical fluctuations in rainfalls have resulted in many potent issues such as floods, landslides, and droughts. Considering the current situation and drastic climatic shifts, the world will be hit by several episodes of natural disasters at the expense of numerous lives in no time.
Infinite inventions and discoveries are seen under progress across fields such as astronomy, genetics, and mechanics, all striving towards a common goal: Facilitate humanity in daily life. If the uprising technological developments can facilitate human activities greatly, they can surely aid humankind in protecting the environment. Maybe data science is the solution to these environmental affairs.
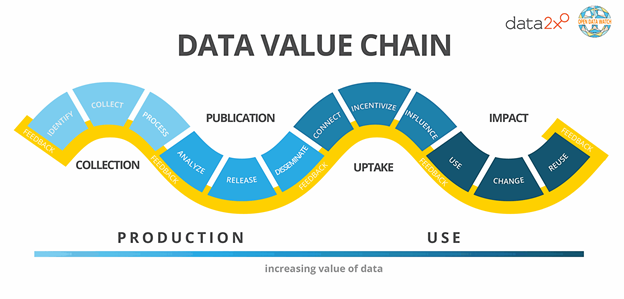
An interdisciplinary field revolutionizing the modern world, data science applies algorithms, computational tools, and machine learning techniques to extract useful information from the available raw data. The data that is worked on can be sourced from multiple channels and be in different formats. It allows rapid processing of data, enabling storage and quick retrieval of a humongous amount of data. Data science is a workflow phenomenon that involves five basic steps to obtain the desired results, as depicted in the picture below.
Data science can offer several benefits to humankind concerning environmental protection that can help us better strategize, frame measures and action plans to minimize natural disasters, protect wildlife and sustain the environment for present and future generations.
It is paramount to understand the critical aspects of the environment and how nature works to precisely utilizing the complex technology to our utmost benefit. This will help us understand how nature and natural processes, in turn, affect human health, food availability, resource exploitation, and influence human activities.
Air Pollution
One of the several issues mankind is facing for decades is air pollution. The air quality has dropped significantly over the years, and access to clean, fresh air is a hurdle. This effect is pronounced in urban areas where forest density is diminishing with the blink of the eye; automobile usage has shown a rapid increase in health-associated conditions such as chronic and acute lung diseases, respiratory disorders, and heart diseases.
System (MCMS) uses sensors and software to instantly measure air quality in real-time, which provides meaningful data.
It works by producing microclimatic data measurements for EPA’ criteria pollutants’ including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and Sulphur dioxide. It also provides provisions for measurements of temperature, relative humidity, and light. Carbon dioxide levels can be measured, whose concentration is one of the prime contributors to global warming. Installing these around the cities can provide crucial statistical data for air quality that can help assess the air conditions and carry out valuable measures to deal with global warming and bad air quality.

Threat to Wildlife
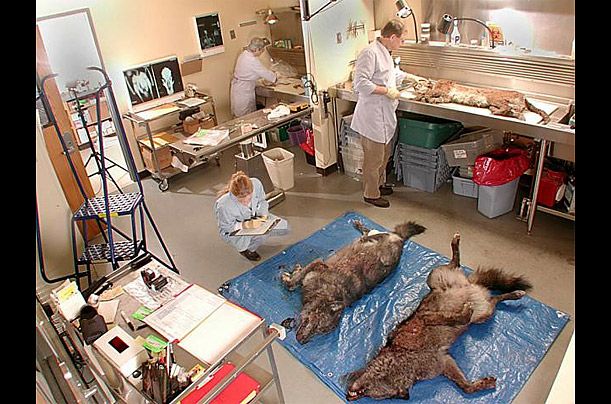
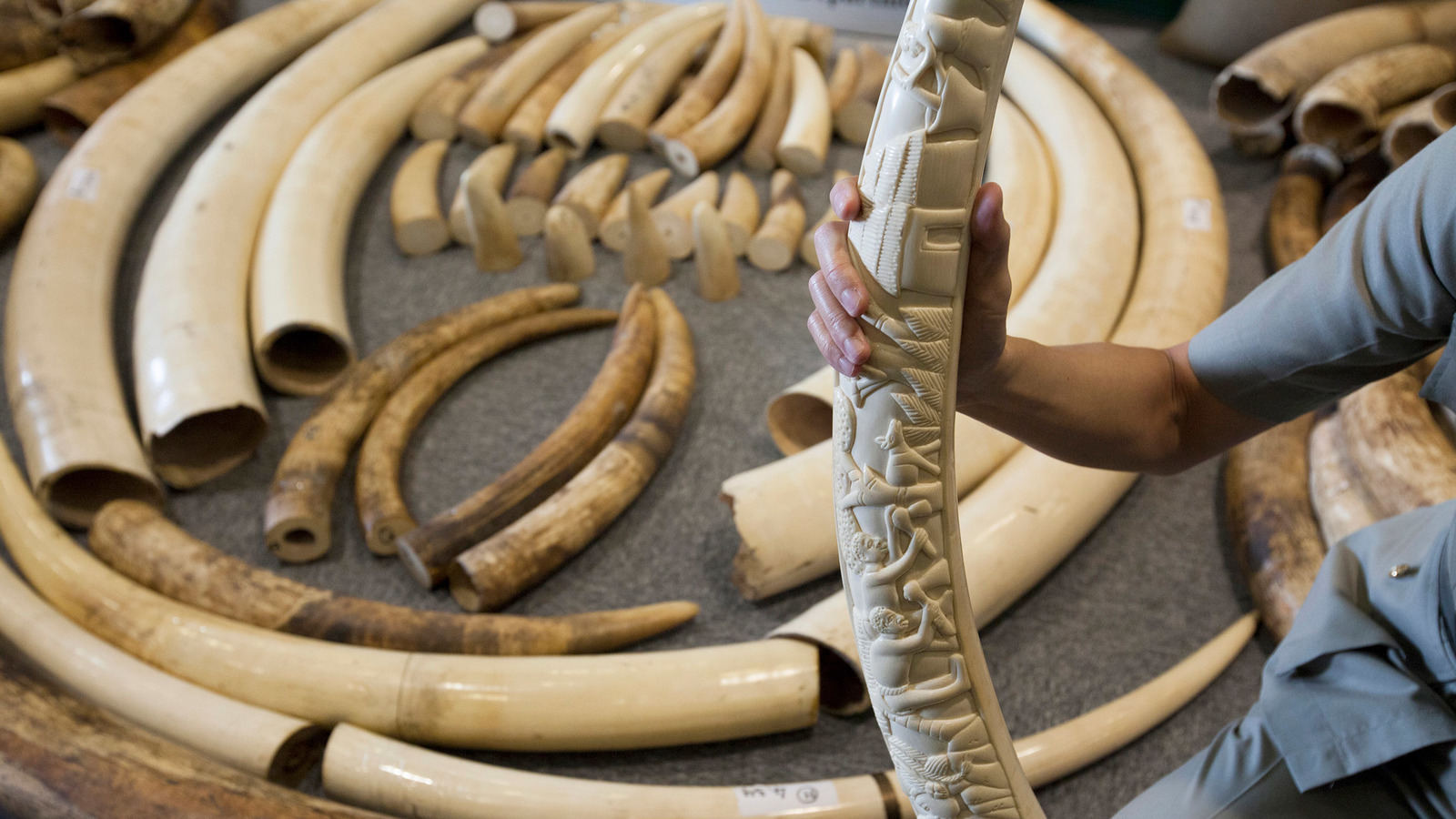
Humankind has been a perilous threat to wildlife. Activities such as hunting, poaching, animal trafficking, and overfishing have devastated the number of species left. Biodiversity and species richness have deteriorated. The current statistics for wildlife degeneration indicate that this matter should be dealt with urgently to save and conserve the wildlife in their natural habitat.
Data science can be a potential source for the conservation of wildlife species of animals. The Nature Conservancy in Massachusetts and the University of Massachusetts Data Science for the Common Good Fellowship Program have claimed that it is possible to construct an algorithm that captures and sorts out trail camera images of animals even if animals’ eyes are only charged at nighttime.
For a better insight into the movement pattern of several animals, motion-sensitive technology is also employed. Such information is then interpreted by data scientists and used to conserve and restore the natural habitats of these wild animals.
Once the natural habitats of these animals are restored, poachers and hunters can be kept away from the specific area that halts the lingering threats. Furthermore, if any tagged animals go astray or lose track, they can be directed back to their habitat.
Predicting Natural disasters
Approximately 207 natural disasters occurred globally in the first six months of 2020. 95% of the losses and destruction were due to weather-related disasters. These climatic shift-induced disasters cause temporary losses and leave behind a copious amount of destruction that takes several months post-disaster to clean and restore the area. The destruction and devastation are marked with the loss of lives, loss of crops leading to food shortage, lack of availability of clean drinking water, and demolished homes and business setups, all exhausting the economy and the life of the inhabitants.
However, these natural disasters do not always come unannounced. Data science can predict their occurrence, including hurricanes, cyclones, and floods. It uses the data of previous hurricanes; the intensity ranges provide an idea about the prevalence of upcoming disasters and the area it is most likely to hit. All this pre-requisite knowledge enables inhabitants and local governments of the hurricane-prone area to carry out suitable measures.

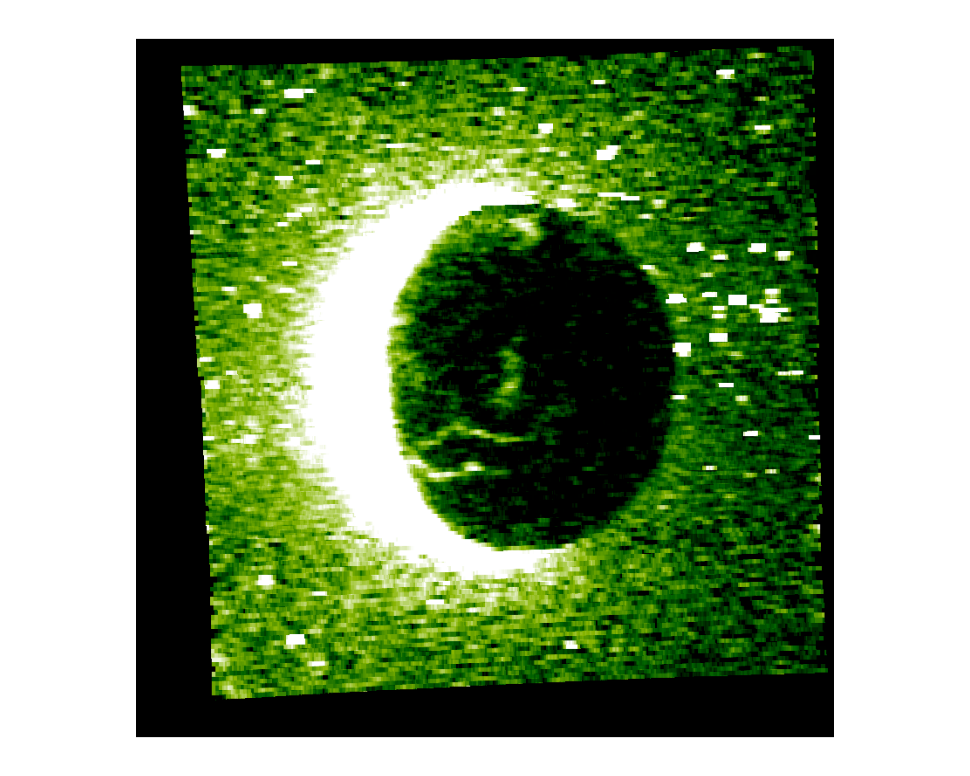
Moreover, satellites such as GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) observe the direction of the hurricane current and track it, producing hemisphere images at fixed time intervals. These computer algorithms also detect its occurrence point, called the “eye of the hurricane.” All these data aids in constructing a model that aids in predicting the hurricane pattern and its path. Today, a few of these predictive models include the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecast (ECMWF) and National Weather Service’s Global Forecast System (GFS) models.
Floods are a common and catastrophic series that come into action for several reasons: unpredictable rainfall, overflowing rivers, damaged dams, and storm surges. The demolition due to floods can be minimized if sufficient flood forecasting data is available and appropriate actions are carried out ahead of time. Satellite imaging from sources such as the Global Flood Detection System (GFDS) and aerial topography plays a vital role in apprehending the overall flood dynamic.
Computer algorithms and machine learning techniques can predict the flow rate of water, the temperature and humidity levels near drainage sites, the soil moisture content, real-time rainfall monitoring, and much more. These details provide a better idea about the flood occurrence time, severity, and the specific locations where the probability of occurrence could be highest.
Earthquakes study and observe primarily by seismologists. Though a formidable candidate to be predicted, scientists are finding ways to foresee the origin of seismic waves using machine learning. By utilizing details about seismic signals, their path of travel from source (location) and the magnitude of the earthquake, data scientist strives to unveil ways to predict the earthquakes. Johnson, Los Alamos National Laboratory seismologist, when asked about his view on the use of machine learning to forecast earthquakes, said, “I can’t say we will, but I’m much more hopeful we’re going to make a lot of progress within decades. I’m more hopeful now than I’ve ever been.”
Water Pollution
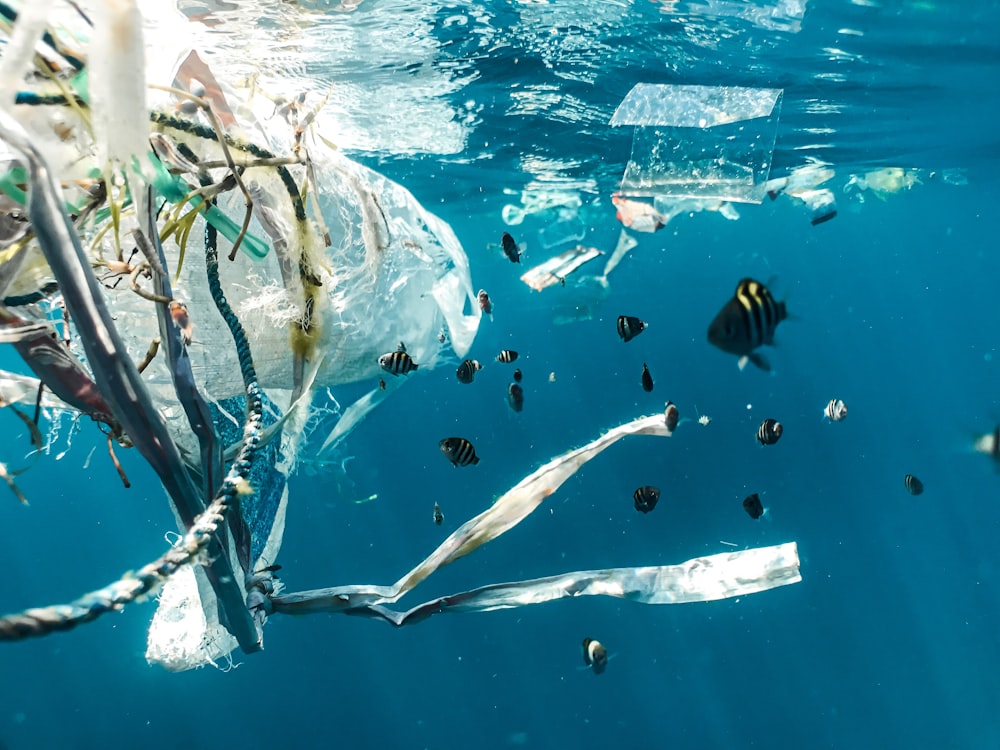
Pollution in water sources is a matter of grave concern for both marine life and water quality. The discharged effluent (oils, toxic chemicals, plastics, harmful metals) ends up in oceans and rivers that threaten species’ habitats.
However, machine learning can provide an easier way to clean seas, rivers, and other natural water resources to restore their original conditions. Microsoft utilizes scientists’ access to AI and machine learning technology to protect the environment and save the planet. One such project is the “Ocean Cleanup,” where the focus is on shrinking marine plastic and additional slew issues. Locating and identifying heaps of debris is made easier using AI, which saves time and labor work. This initiative aims to partner the identification system with an automated collection unit to accumulate plastic for its systematic removal.

Though data science seems to have a bright future being utilized as a critical tool in environmental protection, further advancements and polishing must make it a sustainable practice. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has marked 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs), which should form the basis for using data science to protect the environment and make it sustainable.
Furthermore, the practical application of data science for environmental protection requires a hefty sum of financial input and resource usage, proving challenging for developing countries. It is preoccupied with other large-scale issues such as combating hunger.
Moreover, highly educated individuals possessing profound intellect are needed to interpret the AI results to make good use of them accurately. Attaining such a high level of education and mastering the skills required specifically for this domain puts a strain on the finances. Another aspect that needs attention is that although machine learning is automated, it is prone to high error rates. Some errors are kept unfound, and they continue to influence the downstream results of the chain process, thus depriving the data scientist of the accurate picture. Such anomalies can take a significant fraction of time to be detected and then restored.
However, the scope of this technology in different fields of life, especially environmental protection, is paramount. Further developments and advances will enable us to uncover new features that might solve the big obstacle humanity is facing in the modern world.
“The goal is to turn data into information, and information into insight” – Carly Fiorina.
References:
- https://data-flair.training/blogs/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-machine-learning/
- https://www.environmentalscience.org/data-science-big-data
- https://medium.com/rs21/4-ways-data-science-is-driving-innovation-to-help-the-environment-348f79bc44c
- https://bluepes.com/blog/data-science-usage-in-natural-disasters-predictions/
- https://datapopalliance.org
- https://bluepes.com/
- https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/a-running-list-of-record-breaking-natural-disasters-in-2020/
- https://www.investopedia.com/natural-disasters-cost-usd210-billion-worldwide-in-2020-5094629
- https://www.nature.org/
- https://www.intel.co.uk/content/
- https://www.analytixlabs.co.in/blog/data-science-life-cycle/