Human knowledge of the natural world is improving day by day. Amazing discoveries have been made in vastly spread space and from under the lens of the microscope. Each passing year leaves behind a pile of scientific research and information. The year 2020 held its significance for being more focused on medical and biological sciences research. Experts around the world were challenged with the task of Coronavirus vaccine development. Like many other countries worldwide, experts from Pakistan also conducted valuable research on COVID-19.
Apart from COVID related studies, medical science research in general was quite fruitful. From the winning of the Leibniz prize by Pakistani origin biologist Asifa Akhtar to Mishal Khan’s appointment to the governing body of London School of Tropical Hygiene and Medicine, Pakistanis rocked the stage everywhere. In the coming paragraphs, we’ll discuss some of the most prominent medical science discoveries, and innovations are done by Pakistani researchers in the year 2020.
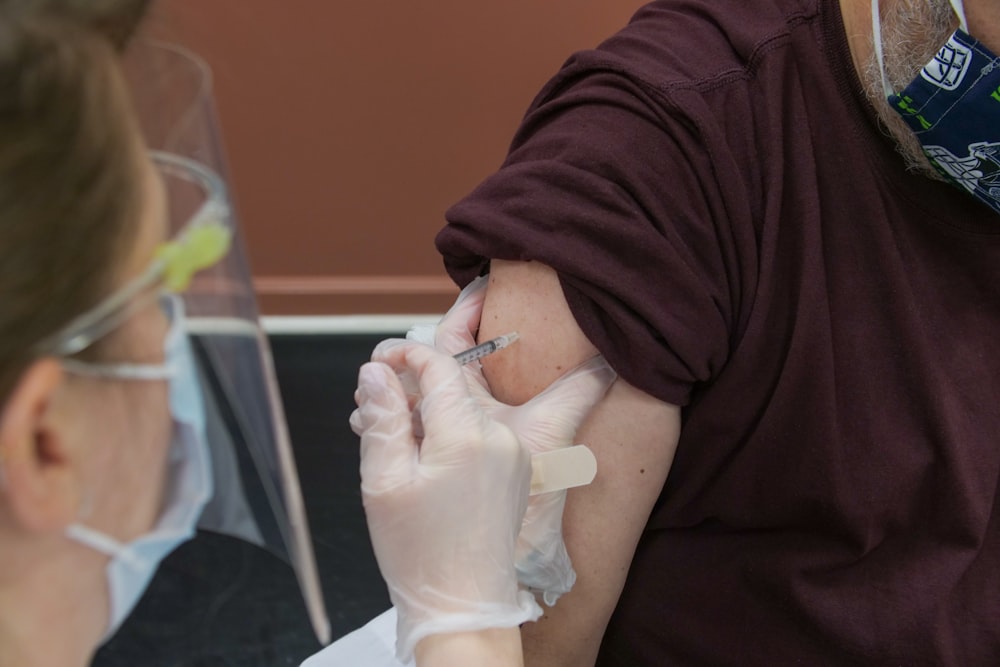
Pain-free Injections
Many adults and children have trypanophobia – the extreme fear of needles – which leads to resisting or denying simple procedures like an intravenous drip and even essential vaccinations.

Realizing that trypanophobia is a real problem, a fourth-year student at AKU’s Medical College, Ibrahim Sajid, has been striving to find a solution. Over the past four years, he has worked with a range of emergency medicine specialists, product designers, phlebotomist,s and nurses to develop a prototype ‘pain-free, invisible’ method to deliver injections that will begin human trials soon.

Research shows that the sight of needles accounts for 70 percent of the fear. Simultaneously, the actual prick sensation contributes to the remaining 30 percent, which is why any offered solution should focus on both visual and sensory stimuli.
Ibrahim has tried various low-cost options like a Japanese hand fan and detachable cardboard sleeve to hide the injection from patients, thus controlling the visual stimulus. For the actual sensory stimulation, numbing cream and bio freeze was tested on various patients.
This innovation won him the ‘Global pediatrics researcher Investigator Award.’
NUST’s Cardiac Stents production
Scientists of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, finally developed cardiac stents in 2020.
Dr. Murtaza Najabat Ali worked on this project individually for 11 years and with his team for another 3.
The locally produced stents were tested extensively compared to their international counterparts and be at par with the imported stents’ clinical performance. The tests were carried out in different renowned centers of Germany and Poland.
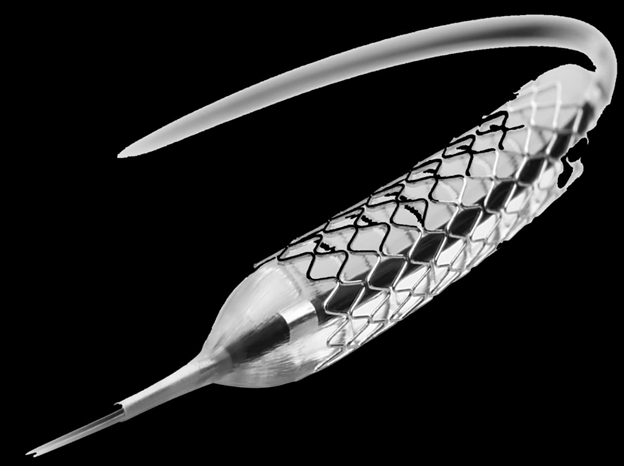
A facility has also been inaugurated. The facility – ‘N-ovative Health Technologies’ has started mass production of cardiac stents and angioplasty balloon catheters for the general public at affordable prices.
Discovery of New Meningitis Sign – Stiff Neck
Prof Shahid Jamil and Dr. Syed Shahmeer Raza’s of Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, carried out a study to introduce and validate a novel clinical sign in Meningitis. It was accepted for abstract presentation at the Royal College of Physicians (RCP) London Conference to be held on 8th December 2020.
The introduction of a new clinical sign is Neck Stiffness in Lateral Position (NSLP) named Jamil’s Sign after the Principal Author: Professor Dr. Shahid Jamil. The observation leading to this study was the effect of change in posture that a person resists when the Neck Stiffness (NS) is checked in Supine position. This resistance was observed to be far more than when the same change in posture was brought about in the Lateral Position. Throughout his career journey, Dr.Jamil has come across more than 3000 cases of Meningitis.
Jamil’s Sign’s pathophysiology could be similar to examining the tone in different parts of the body. The concept is to look for an increased tone in the neck muscles under the influence of meningeal irritation. The maneuver will lead to a motor response as a result of nociceptor exploitation. This motor response is gauged in the form of neck stiffness.
Jamil’s sign removes the effect of gravity and passive resistance to the neck movement observed in the supine position.
Recombinant B- Lactamase production:
A recombinant ß-lactamase has been produced from Bacillus subtilis R5 using Recombinant DNA Technology during a research study at the Institute of Biochemistry and #Biotechnology, the University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore.
Despite resistance, ß-lactamases hold several useful applications in the pharmaceutical industry, wastewater treatment plants, diagnostics, food analysis, and cancer treatment for the targeted drug delivery to cancerous cells. In Pakistan, there is no single unit for the production of ß-lactamases, and this enzyme is being imported for diagnostic purposes.
The researchers aim at producing this ß-lactamase in bulk. Still, it needs funding for its large-scale production and its testing at various laboratories before its commercial level availability.
Local production of ß-lactamase will save massive foreign exchange for the import of this enzyme.
Pakistan’s First Affordable and Bloodless Dialysis Machines
Byonyks developed Pakistan’s first bloodless risk-free dialysis machine with the collaboration of the Ministry of Information, Technology, and Telecommunication. Byonyks’ unique technology does not require extracting blood out of the human body to perform dialysis. Patients can perform bloodless dialysis at home without any supervision with protection from life-threatening infections.
Pakistan is the 5th country globally to have its indigenously produced “Bloodless” Dialysis Technology after the United States, Germany, Japan, France, and China.
Study on CLN5 mutations
Two previously-unknown mutations in the CLN5 gene were reported to cause CLN5 disease, a form of late infantile Batten disease, in a new study. The study also represented the second-ever publication describing CLN5 illness in Pakistan, hinting at a more worldwide distribution of the condition than previously thought.
The results, “Novel likely disease-causing CLN5 variants identified in Pakistani patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis,” were published in the Neurological Sciences Journal.
The new study describes two Pakistani families that were found to be affected by CLN5 disease. In both families, the parents were consanguineous (biologically related to each other). The two oldest children have been affected by one family: a 10-year-old girl and a 7-year-old boy. Both children experienced a similar progression of symptoms, including memory loss, difficulty moving, loss of vision, and speech impairment, which started to emerge at 6–7 years of age and progressed over time.
Late infantile Batten disease refers to Batten disease in which symptoms manifest in childhood, usually at the ages of 2 to 8. CLN5 disease is a form of late infantile Batten disease caused by mutations in the gene CLN5. The disease was initially identified in northern European populations in the late 1990s. Since then, research has revealed the presence of this disease elsewhere in the world as well.
Speedy Recovery of Diabetic Chronic Wounds
Nanomedicine, in combination with some hormone or oxygen-producing agents, can improve diabetic wound healing. Oxygen-carrying nanocomposites can also enhance chronic diabetic wounds’ recovery rate by supplying the oxygen upon external stimulation.
Sodium percarbonate (SPC) is one of the potent peroxide-based oxygen-generating materials that have been found useful for the treatment of dermal wounds. SPC is a moderate water-soluble salt (<0.01% at 20°C) that releases hydrogen peroxide and ultimately oxygen on decomposition. No one has investigated its effectiveness for the treatment of diabetic wounds models yet, so this study was aimed to explore the therapeutic features of SPC for diabetic wound applications.
In the present study, PCL polymer matrix based electrospun nanofibrous wound dressings loaded with inorganic SPC salt that can chemically generate oxygen in-situ were used.
The study included assessing sustained oxygen release from prepared dressings for a minimum of 4 days, followed by evaluating their efficacy through in-vitro cell studies and a CAM assay to evaluate their angiogenesis potential and healing response of a full-thickness chronic diabetic wound rat model.
First Stereotactic Surgery
For the first time in Pakistan’s history, an 11-year-old boy possessing a 10cm tumor in the brain was saved using a compassionate and complicated technique of stereotactic neurosurgery. The procedure was performed by Dr. Sattar Hashim, a renowned neurosurgeon at the Neurospinal and Cancer Care Institute (NCCI) in Karachi.
Stereotactic neurosurgery is a form of surgical intervention that locates small targets inside the skull using a three-dimensional coordinate system and performs several types of procedures on them. Under this procedure, a tiny hole was drilled in the child’s brain, and a 200 ml tumor was extracted through a syringe
Antibody Treatment for COVID-19
The C-IVIG therapy uses immunoglobulin (IG), a blood product extracted from the plasma of people who have recovered from the infection, rich in the antibodies that target the virus. Continuous infusion of immunoglobin can neutralize the condition in patients and shorten the course of the disease.
Pakistan is on the threshold of becoming the first country to carry out research. It is mandatory to introduce intravenous immunoglobulin (C-IVIG) therapy at a mass level as ‘severe’ patients under treatment for coronavirus have a 100% recovery rate.
Scientists at the Dow University of Health Sciences (DUHS) in Karachi, who are conducting clinical trials of the C-IVIG therapy for the treatment coronavirus, have said that the trials were very encouraging and remarkable.
Pakistan was the first country to develop the immunoglobulin solution in April 2020
Brain Controlled Bionic Arm
Pakistani Software Engineers (Muhammad Umer Tariq, Muhammad Umar Lodhi, Umair Ahmed) invented a Bionic Arm controlled by human thoughts. Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is used for manufacturing this arm along with Image processing, Machine learning, Artificial intelligence, Networking, Mechatronics, and Hardware development.
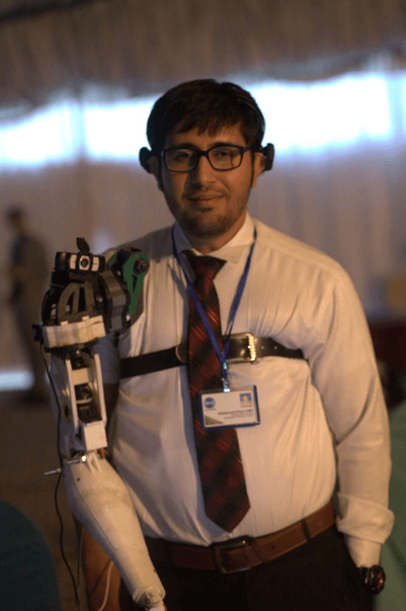

This system is capable of sensing brain signals using active electrodes placed non-invasively on the subject’s head. As the accuracy of non-invasive brain-computer interfaces is very low. They improve the accuracy of non-invasive brain-computer interfaces by applying Image processing, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Networking.
Using this system, no internal surgery of the brain is required for placing the electrodes invasively inside the brain. This system can be easily installed on a person who has no arm from the shoulder joint. This bionic arm is created for a worst-case scenario. It has nine joint movements (shoulder, bicep, elbow, wrist, and five individual fingers)
World’s first Portable MRI Machines
New York-based company called ‘Hyperfine’ has acquired 501(k) clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the world’s first-ever portable MRI scanner. The FDA accords the 501(k) clearance to those devices that demonstrate that not only are they useful, but they are safe for public use as well.
Hyperfine is an initiative of a Pakistani-American Radiologist, Engineer, Serial Entrepreneur, and Healthcare professional, Dr. Khan Siddiqui. Although the portable MRI machine’s weight is around 635 Kgs, it is almost negligible compared to the 4,500 Kgs of a typical 1.5T MRI machine. A 3T MRI scanner weighs even more at 7,500 Kgs.
What makes this MRI scanner portable is the wheel array at its bottom. Anyone can maneuver the machine through the wheel array without having to push 635 Kgs from room to room. Besides, Lucy’s point-of-care MRI – as the portable device is known – will consume 35-times less power than the traditional MRI scanner.
Discovery of Factors involved in the transmission of trauma effects
Research effort involving Pakistani neuroscientist Dr. Ali Jawaid identified a role for metabolic factors in transmitting the effects of traumatic experiences from parents to children.
After previously showing that adverse exposures in parents’ early life can lead to many psychological and metabolic perturbations in the children, he & colleagues have now demonstrated that the main culprit behind the transmission of these effects is certain chemicals called metabolites in the blood of parents.
These metabolites include chemicals released by the brain, liver, and other organs.
They first studied trauma in a mouse model where the newly born pups face separation from their mothers and are raised by stressed mothers, similar to many childhood adversity cases in humans. They found that this traumatic exposure affects many metabolites, especially fatty acids in the blood.
They further show that these altered fatty acids make their way to the sperm cells and change a nuclear receptor’s activity, an essential regulator of gene expression. When the offspring is born, it has an altered metabolic makeup and responds atypically to periods of high sugar intake or starvation.
The most notable aspect of the study is its relevance to humans. While the central part of the study was performed in Zurich, for the human part, Dr. Ali Jawaid traveled to Pakistan and collaborated with the SOS children’s’ villages. Together with a team of dedicated students, he studies children who had endured early life trauma in the form of paternal demise or maternal separation and found similar alterations in their blood.
References:
- https://www.aku.edu/news/Pages/News_Details.aspx?nid=NEWS-002416
- https://tribune.com.pk/story/2268590/nusts-locally-made-stents-hope-for-poor#s1/
- https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/embj.2020104579
Also, Read: Neuaralink; one microchip fulfilling hundreds of possibilities