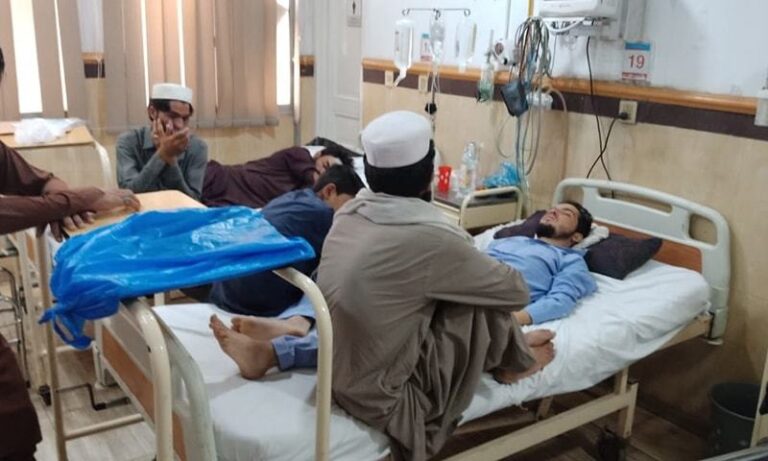
We all are aware of the ongoing pandemic crisis, be that fact or baseless WhatsApp fast forwards. But we know very little of the second pandemic we are going through “Global Mental Health Crisis” that has, to be more specific, affected greatly our healthcare professionals who have been on the frontline for almost half a year now. Unfortunately, this isn’t new to them. For doctors and paramedical staff, depression, burnouts, and excessive workloads is not a unique experience. Studies from the early 1990s found that the risk of suicide was very high among American physicians, specifically female physicians. But this time, it’s very likely for them to have elevated stress levels considering the ongoing situation.
Why are HealthCare workers most dramatically affected?
Everybody is having a hard time dealing with their mental health issues. People stuck at home in abusive relationships, patients suffering from General Health Anxiety and OCD, those who’ve lost jobs, most importantly people who’ve lost their loved ones to Covid-19. Why emphasize on health care workers?
Not starting from zero
They are not starting from the zero line. Anxiety, high stress and depression has been a part of the medical professions since times unknown. Burnouts and high workloads have already been putting their mental health at stake and a global health crisis where they’ve to endure grueling shifts, increased number of casualties to witness and difficult choices to make. Hence we are definitely not talking about sudden induced stress levels, we are talking about elevated stress levels to a point that could render a person with decreased function and exposed to addictions and drug abuse as failed coping strategies.
“Workload has doubled. I’m stressed out. But the worst was witnessing three of my young patients die of Covid. The youngest is 21, with no underlying medical condition. That took a huge toll on me.”
Difficult choices to make
Most of them had to endure the torment of making difficult choices and painful decisions. Whether that be the common question for every healthcare professional out there;
“Choosing to care for my health, my family’s health or to serve the critically ill without concerning the former options.”
Or be that the choice of which patient has to be put on a ventilator and which one can they put into arms of death, considering the shortage of ventilators and other necessary medical devices.
‘I’ve been worried about my critical patients that we can’t do much about.”
He Is a medical officer in HMC, Peshawar who has tirelessly served Coronavirus patients.
Social stigma & Public Attitude
Social distancing has been the new normal for months now. But that doesn’t necessarily mean adapting humiliating behaviors towards health care staff in your neighborhoods or in general public. This young doctor from Peshawar displayed discomfort on how they’ve been looked at while they put their lives in danger for the people around them:
“People, even close relatives, look at me in disgust only because I have served patients suffering from Covid and got infected myself and later had to go through the torment of seeing my family suffer from Covid too. All because I chose to serve my people.”
On being asked about what he had to say about the public’s attitude towards this grave condition, he enlisted all the factors that were contributing to the severity of the ongoing crisis. But to my surprise he said it had its pros too. Upon being asked he stated;
“Finally the respect has doubled. They know our importance now”.
It’s sad to know that it took us an entire pandemic to stop labeling doctors as “Butchers” and start giving health care professionals there due respect.
“This is not only work but exposure to the already hollow psychology of society, which got more obvious in these times, that makes it hard to find a reason to work out there.”
The endless guilt trips
Those who are fighting on the frontlines suffer from the guilt of putting their families at risk. While those are not on the frontline are guilty about not being there for others. They are guilty of things they don’t even control, to enlist a few; the hurdles in their career growths and job opportunities. A young ambitious doctor from Islamabad, who was about to start her job in the UK and was determined to serve people, is going through high levels of stress as this pandemic proves to be a hurdle in her way and that she has to stay home in a time where hospitals are in dire need of doctors.
“Yes it has been a hurdle. I’ve been applying for jobs in the UK. But due to the pandemic the process is extremely slow. In fact they had stopped taking doctors from outside for almost 2 months. But now the recruitment process has started again. But the uncertainty is really making me go crazy.”
The added guilt of infecting family members has elevated anxiety and doctors complain their brains are constantly in a fight-or-flight mode, which drains you out. Dr Maeeda from Cantonment General Hospital, Rawalpindi had this to say;
“It’s very stressful, worrying about getting it and bringing it home. Being strict with SOPs while a layman doesn’t care about their and our health.”
Distancing from their families
Out of the sheer fear of getting their families infected doctors and nurses had to stay away from their homes, some residing in garages and some at hotels. Not seeing or meeting your loved ones can highly affect one’s mental peace. A young doctor who got infected himself and his family members as well had to say how hard it was to stay away from his little doctors
“Had to stay away from my daughters for 45 days straight. That was very hard.”
Keeping Up with the stereotypical image
As doctors, there is a certain, stereotypical image of a calm and neutral “hide-away-your-emotions” kind of a person that they must maintain. This leads to bottling up of emotions which can have disastrous effects on doctors’ mental wellbeing. Opening up about your emotions and worries would bring along the risk of being no more a trustworthy doctor for patients. As the social stigma regarding mental health prevails here too where you are labeled crazy and not well enough to deal with patients. A proof to this is that most of the doctors I interviewed chose to stay anonymous because they had to show and portray that they are strong and unaffected and that their families might worry more after reading what they are actually going through.
Moral Injury; borrowing a military term
Moral Injury refers to an injury to an individual’s moral conscience and values resulting from an act of perceived moral transgression, which results in profound emotional guilt, shame and moral disorientation. In context to the field of medicine, it might refer to the Hippocratic Oath that each doctor takes. Moral injury in such times won’t be surprising for doctors. As a business side of the health care system and lack of proper devices e.g., a ventilator might cause doctors to make difficult choices and consequently paving a way to moral injury.
Added torment on getting your religious beliefs questioned
In Pakistan, a problem doctors faced was getting their religious belief and tawakkul questioned because they asked people to avoid congregational prayers and suggested they perform their spiritual practices at home. People refused to isolate socially and made fun of those who did by labeling them cowardly and stating they had a weak belief system. This added to the numerous factors causing distress and social humiliation to the healthcare staff.

Unhealthy behavioral patterns among healthcare professionals
Upon asking from different doctors the same question;
“How has this pandemic affected your mental health”?
“Severe insomnia. I can’t sleep at all. I’ve to take sedatives regularly. Secondly, anger issues! I was never this short-tempered. Workload has doubled. Nightmares are now regular. I try to travel to our house in Nathiagali for peace of mind even if I hardly get one day as a break.”
“My brothers, my niece, my sister in law and I myself got infected and seeing the little one suffer has taken a toll on me.”
“I’ve noticed strange behaviors and high levels of stress among my colleagues. I’ve seen some of them coming in mismatched clothes or someone brought a white shirt thinking it was his white coat. Everyone seems to go crazy. The workload is definitely taking a toll.”
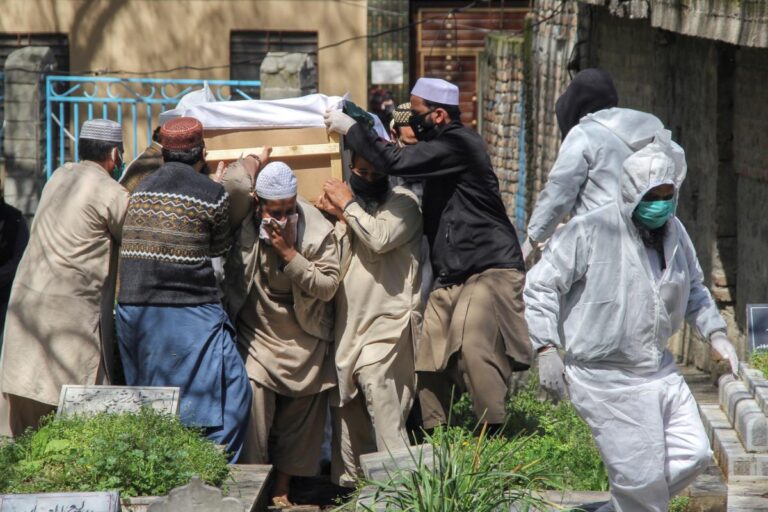
“Seeing people die, especially young ones is hard. My colleagues and friends have suffered due to it but the hospitals won’t let out proper data and statistics of the doctors infected or dead.”
“Regarding mental health, it can be divided into ‘Emotional, Psychological and Social’ wellbeing. Talking in context to emotional wellbeing, doctors have emotionally collapsed. It’s not easy seeing your family, friends, and relatives die in front of you while you are unable to do anything. Now talking of psychological and social wellbeing, you can understand a person working double the shifts plus double the workload. He can’t think about spending time with your friends or family. Nobody, even your best friends, don’t want you to visit them because you’ve been assigned to a sampling unit or ICU. It is hard. No place for social or psychological well being.”
One-to-one conversations with Dr Iman Zia & Dr Hibba Noor Vardag
Dr Iman Zia is a young doctor who had the chance to work as a healthcare assistant at Field Isolation Centre at Expo, Karachi. Her sister took to social media and described her plight witnessing her sister go through tough ordeals.
She wrote in an instagram post that;
“In these awfully difficult times, where one wants to be home and safe, my sister was volunteering at the Field Isolation Centre at Expo. Risking her life to treat patients is something that takes a lot of her courage. She has been away from home for almost a month and has spent her time serving the nation.”
( Link to the original post: https://www.instagram.com/p/CBdwx-7JCBo/?igshid=1majyvzk38obn )
On asking Dr. Iman herself about how it has been for her to be on the frontline battling disease and death. She had to say this;
“Working during this pandemic has been a huge responsibility which healthcare workers have dealt with by staying calm, suppressing our emotions, for the sake of humanity. But we have been overburdened with stress, anxiety, and fear during the pandemic crisis.”
What has this pandemic changed?
“It’s surreal how this pandemic has changed people’s perception of death. How fear has replaced grief.”
What do you think about people’s attitude towards such a grave condition?
“Looking at people not following the SOPs feels miserable.”
How has it been for you and your mental health working at Field Isolation Centre Expo?
“There have been sleepless nights thinking about what happens next and feeling cranky after hours of wearing PPE. Mainly there has been a wave of fear, to avoid passing the risk of contracting the virus to our family members.”
Dr. Hibba Noor Vardag is a fresh graduate from Khyber Medical College, Peshawar. She had to start her house job at KTH, Peshawar during this pandemic. She took the start of her career in many unexpected circumstances, which definitely had its effect on her.
“How did the ongoing health crisis put your life on hold while you were about to start your job?”
“Always having a hectic schedule and then suddenly sitting at home, doing nothing had a not so good impact on my mental health. Got into unhealthy habits, over-sleeping, lesser productivity, and overthinking about every single thing which is emotionally draining.”
“You started your house job in very unexpected circumstances, how has that had an effect on you?”
“Of course it affected our career start very badly, we couldn’t practice that well, the patient influx was very low, missed all the important “busy” morning rounds and suffered from severe OCD due to the pandemic. Most importantly, our excitement got ruined.”
“How’s your learning experience suffered?”
“Currently I’m working in Gynae, the obstetrical procedures are not affected that much. But the gynecological procedures are totally at pause, so our training has been badly affected. The patients suffer a lot too.”
“How do you see your fellow doctors being affected?”
“Doctors have been exposed to a lot of sufferings during the pandemic. There is always a fear in our minds before approaching the patient who affects our output. Elective procedure on hold, training affected badly, and over our community is mentally and physically exhausted.”
Why is “Hero-worshipping” not enough? How can we help?
Social media has been flooded with posts that came out in support of our front line “heroes,” people clapping in their balconies and the government “only” appreciating our healthcare staff and numerous other ways where we’ve been hero-worshipping them. But what we need to understand is that there is a significant problem we are missing out on. Calling them heroes and clapping in appreciation is wrong on so many levels. The problem with this narrative is that it’s accentuating valor as “to work in hazardous conditions selflessly.”
While the hazardous conditions shouldn’t have existed in the first place and they exist as a result of the failed responses from government and administration bodies worldwide. This narrative creates a notion that those who are not willing to work in any more hazardous conditions to be looked down upon because they choose their safety and their family’s safety due to the scarcity of PPEs. Appreciating them and acknowledging their sacrifices is no harm, but only sticking to hero-worshipping rather than taking some concrete measures is no good.
Pay heed to what doctors and research scientists tell you. Stay home stay safe. Take care of health care professionals, reach out to them, and diminish the taboo about them being stereotypically calm while there is an entire health crisis going on.
Also, read: CORONAVIRUS; the current catastrophe of our lives