Today, when the world is gripped by coronavirus’s devastating and vile effect, the crossroad of technology and healthcare system has given life sciences a new dimension. In the past, when the innovation of even a spectroscope would take gazillion years, now with the advent of Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning, and Internet of Things, we see large scale digitalization of data; development of personalized medicines, 3D printing of organs and lifesaving surgeries being executed by Robots. Doesn’t it jolting, like if some giant virtual power took over the world miraculously?
Now the world is in the swirl of a killing virus, taking lives of thousands each day; an invisible creature challenging to contain, the technological revolution has also paced fast in the previous years that we are now equipped enough to computationally visualize structure and leading for the preparation of a potential vaccine. Evolving from an era when even pneumonia was considered malicious, we have grown to a stage of telemedicine.
Not that this amalgam has brought changes on a grand level of vaccines and surgeries, the layman has benefited from this amicable relationship. From data automation to telepathy to personalized medicines, these are all groundbreaking evolutions. Personalized medicine has been customized according to an individual’s genetic makeup, hence shifting from the paradigm of “one size fits all.” Gone are the days when we used to wait for hours to get reports of our sample, now it takes just one click, and we can get an email on our phone screens. During the pandemic, when people are afraid to go out to the hospitals for a usual checkup, virtual consultations with their specialists are lifesaving. Not only are the patients getting the perks, but it has also brought convenience to the doctors and the clinical staff. The need for pen-paper to make records has become history, and the electronic record has taken its place.
Technology has revolutionized the healthcare system in other parts of the world as compared to Pakistan, we can witness a huge difference. Pakistan being a third world country, already swarmed in the financial crisis, finds these technologies a luxury. A few parts of our country like Thar and Balochistan have a severe lack of basic necessities of life like water, food, hospitals, and students are continually protesting against mere internet facilities. So, we can’t expect the same level of revolutionary impacts of technology in a country like this compared to the developed countries. Having said that, we can’t completely disprove the benefits we are getting from this wave of revolution, not to the scale of robots doing surgeries, but we have seen remarkable growth in some departments like automation of data and telepathy very furiously making its way to the industry.
To get into the details of how this technological revolution has impacted the health care systems globally, we will discuss some of the departments where exponential growth is witnessed. Some of them are:
Digitalization of Data
Electronic health records have proven to be game-changers in the medical world because they have eliminated the need for maintaining paper records. Massive data can be stored in a more organized and safer way. This digitalization provides comfort to the Medical assistants, medical coding professionals, registered nurses who have a handful of roles, and the patients; patients can access their medical records in just a single click, which makes the retrieval of data accessible smooth, and less time-consuming.
Digitalization of data has several benefits to the health care system:
- Using EHR, physicians can get an automatic alert about the potential issues (such as allergies or intolerances to certain medicines) of patients. This alert enables the Doctor to treat the patient accordingly and prescribe drugs, considering the patient’s potential issues.
- Storing data into a single extensive database is less time consuming and efficient with fewer chances of error than paperwork. It also enables the remote working of medically coding experts to increase productivity and efficiency.
- According to a study from the University of Michigan, this new electronic health record system elevated the cost of outpatient care by 30%.
Telemedicine
It allows healthcare professionals to evaluate, diagnose, and treat patients remotely using telecommunications technology. Telemonitoring technology is used to monitor, evaluate, diagnose, and treat patients at a distance using telecommunications technology.
Amid the current situation, telemedicine is a perfect example of how technology is meeting the ends with every day, increasing the needs of at-risk patients. People who don’t have the urgency or dire need to visit hospitals prefer to consult doctors virtually these days and telepathy proved an essential means for this digital consultation.
Telemedicine has several benefits, including:
- It saves time.
- Improved access to remote areas.
- Increased efficiency.
Mobile Health
Mobile health involves mobile technology to monitor and share health information, such as wearables and health tracking apps. These wearables and health tracking apps control weight, blood pressure, heart rate, glucose meters, or diet data. It is the fastest-growing trend in the healthcare industry; google and apple are trying their best to push the limits to the next level by introducing amazing technologies and apps every year.
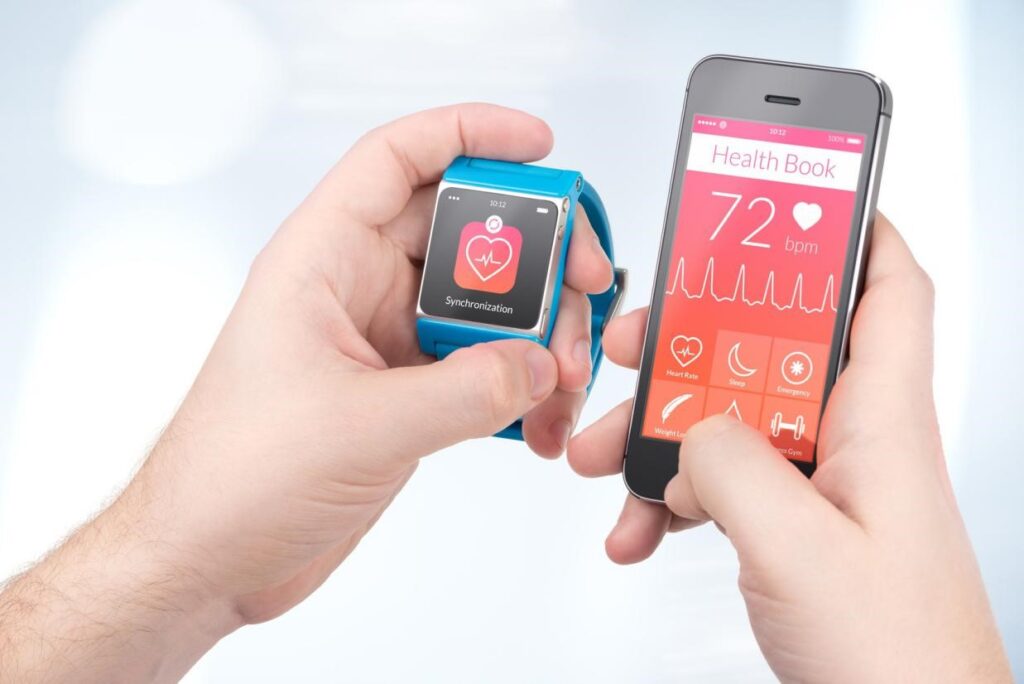

There are a plethora of apps available on the internet that are flexible for both parties, patients, and doctors; also, an inexpensive means to provide better health facilities. This technology proved very beneficial for the people living in remote areas, making health care facilities available 24/7. This technology enables patients to connect with the healthcare provider anytime by sending messages and scheduling appointments for telemedicine visits. It also improves medication adherence; once the patient is discharged from the hospital, health can be used to provide patients features like automated medication, refill reminders, and educational information.
Personalized Medicine
Industry runs on the response of consumers, and the consumers of this age like to experience products specially tailored for them. Same is the case with the healthcare industry, it leans on technology to add a pinch of the spice of personalization to whatever they do; being more precise regarding their patient’s needs.
In the time of EHR, where data is stored and organized on such a grand level, it provides researchers with more opportunities to use it to analyze and evaluate genomic mutations, epigenetics, and other contributing factors leading to different genomic makeup of every single individual. And this analysis is the laid foundation of the development of personalized medicine for each individual depending on his/her lifestyle, heritage, medical history, genetic information, and on the data regarding individuals who faced similar medical problems.
Revolutionizing Drug Development
The pharmaceutical landscape has evolved drastically in the past few years after the advent of silicon drug trials. The process of drug development, its approval, and introduction in the market is quite a long and expensive procedure that requires a lot of effort. However, technologies like AI and insilico trials have improved various aspects of drug development. New drug candidates and novel therapeutic solutions are being developed by companies like Turbine, Recursion Pharmaceuticals, and Deep Genomics, using the maximum potential of AI.
Computer simulations are being done to evaluate a medical product, with the organ-on-a-chip already in use. Institutes like Virtual Physiological Human have developed virtual models for the study of heart disease and osteoporosis. HumMod is another human physiology model used in several projects.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the science of designing and producing materials and devices at the nanoscale; to solve some of the biggest problems in medicine. Lifesciences has expanded its horizon to the extent that it’s now living at the dawn of nanomedicine age. This technology is currently used to transport drugs to specific cells and the nanoparticles used for cancer treatment and tiny surgeries.

Smart pills are one of the greatest innovations of nanotechnology, approved by the FDA in 2001. Ingestible sensor pills are used for monitoring and treatment where drug dosage is adjusted accordingly from data collected from the body. Another exceptional example of smart pills is the one that keeps medication records, specially designed for people surviving schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, these pills enable them to track their medication history via smartphone or seek medical information from the healthcare professionals.
Smart patches would also prove groundbreaking in the future of nanotechnology in the field of medicine. Grapheal, a France based company, has showcased its smart patch that will enable monitoring of wounds and even stimulate wound healing. As the technology evolves with time, we will see the smart pills capable of taking biopsy samples for analysis.
Robotics
Robotics is one of the fastest-growing fields of healthcare ranging from companion robots to surgical robots, pharmaceutics, disinfectant robots, and exoskeletons. In 2019, the world saw its first exoskeleton aided surgery in Europe. Robotics can be applied to aiding nurses, lifting elderly patients, and/or helping patients with spinal injuries.
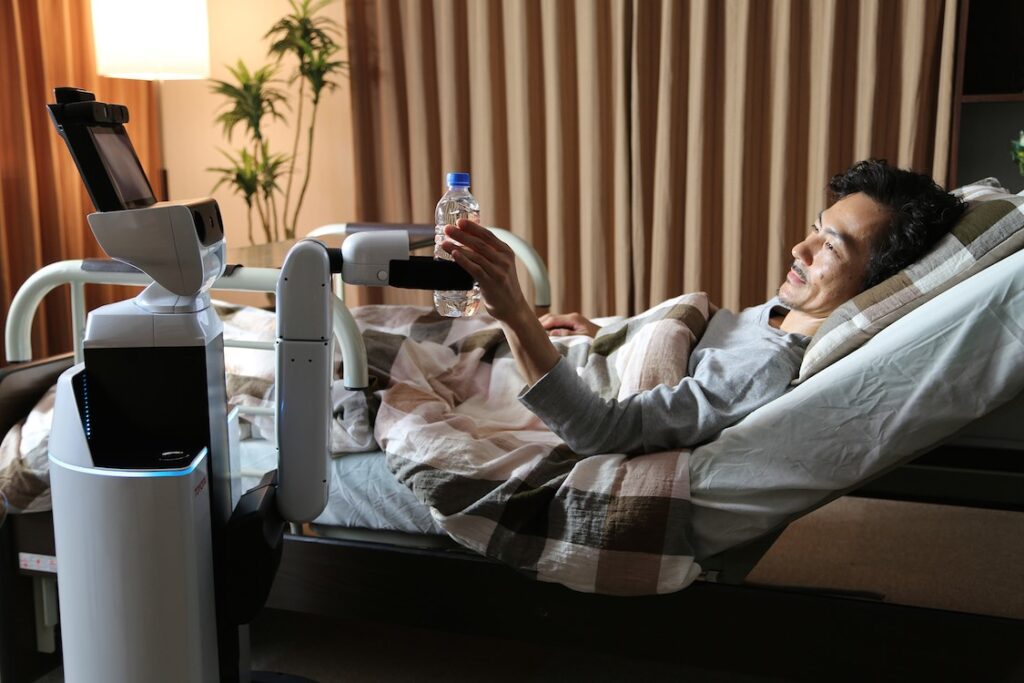

Robot companions like Jibo, pepper, and paro are widely used in the healthcare sector for patients with mental health issues or children with chronic illness. These robots have touch sensors, cameras, and microphones to interact with patients and monitor their medications, temperature, and breathing rate.
The coming years will see more wonders of technology to the health care sector but as it is quoted “one has to be the master of his own house,”
3D Printing of Organs and Drugs
3D printing of bio tissues, artificial limbs, pills, and blood vessels have brought marvelous advancement in all aspects of healthcare. In November 2019, researchers developed a method for 3D print skin and blood vessels that could prove beneficial for burn victims.
3D printing brightens evolution in the pharmaceutical industry by developing 3D printed drugs that have been approved by the FDA since 2015. Now the development of 3D-printing “polypills” is in the pipeline that will be a huge breakthrough, as it contains several layers of drugs to help patients adhere to their therapeutic plan.
Not that all the advancements we have discussed above are in practical use in our country due to the obvious financial strains we have been facing for ages. Technology has played its role to some extent to stabilize our sloppy system with meager resources, making it more accessible and less costly for people around. It is the need of the hour that our decision-makers understand the importance of technology and how it can be used effectively to make the system smooth and affordable.
Only then can we take bold steps on a governmental level, including an increase in the healthcare system’s budget and the training of professionals and other medical staff so that they stay relevant to these technological revolutions. These potential efforts are bound to bring change on a massive scale.
The coming years will see more wonders of technology to the health care sector but as it is quoted “one has to be the master of his own house,” we have to be two steps ahead of the technology so that we do not become its slaves rather be the beneficiaries of it.